114 low relevance results shown for 'Electric'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5 | Next | View 100 per page
Showing low relevance matches only. Return to normal search results
Electrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU219 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Alternative Energies - Energy from a variety of sources can be used to generate electricity ACSCH030 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - Ions are atoms or groups of atoms that are electrically charged due to an imbalance in the number of electrons and protons; ions are represented by formulae which include the number of constituent atoms and the charge of the ion (for example, O2–, SO42–) ACSCH032 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The characteristic properties of metals (for example, malleability, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity) are explained by modelling metallic bonding as a regular arrangement of positive ions (cations) made stable by electrostatic forces of attra ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSPH016 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Heat transfer occurs between and within systems by conduction, convection and/or radiation ACSPH020 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Provided a substance does not change state, its temperature change is proportional to the amount of energy added to or removed from the substance; the constant of proportionality describes the heat capacity of the substance ACSPH022 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Two systems in contact transfer energy between particles so that eventually the systems reach the same temperature; that is, they are in thermal equilibrium ACSPH028 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Some nuclides are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting alpha, beta and/or gamma radiation over time until they become stable nuclides ACSPH029 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Each species of radionuclide has a specific halflife ACSPH030 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Alpha, beta and gamma radiation have sufficient energy to ionise atoms ACSPH039 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is conserved in the energy transfers and transformations that occur in an electrical circuit ACSPH040 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - The energy available to charges moving in an electrical circuit is measured using electric potential difference, which is defined as the change in potential energy per unit charge between two defined points in the circuit ACSPH041 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is required to separate positive and negative charge carriers; charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that can be used to drive current in circuits ACSPH042 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Power is the rate at which energy is transformed by a circuit component; power enables quantitative analysis of energy transformations in the circuit ACSPH043 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Resistance for ohmic and nonohmic components is defined as the ratio of potential difference across the component to the current in the component ACSPH044 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Circuit analysis and design involve calculation of the potential difference across, the current in, and the power supplied to, components in series, parallel and series/parallel circuits ACSPH137 Year 12 Revolutions in modern physics
Quantum theory - A wide range of phenomena, including black body radiation and the photoelectric effect, are explained using the concept of light quanta ACSPH108 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Magnets, magnetic materials, moving charges and currentcarrying wires experience a force in a magnetic field; this force is utilised in DC electric motors ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system ACSCH031 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The properties of ionic compounds (for example, high melting point, brittleness, ability to conduct electricity when liquid or in solution) are explained by modelling ionic bonding as ions arranged in a crystalline lattice structure with forces of attract ACSCH027 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of atoms - The type of bonding within substances explains their physical properties, including melting and boiling point, conductivity of both electricity and heat, strength and hardness ACSPH103 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - A positively charged body placed in an electric field will experience a force in the direction of the field; the strength of the electric field is defined as the force per unit charge ACSPH104 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Point charges and charged objects produce an electric field in the space that surrounds them; field theory attributes the electrostatic force on a point charge or charged body to the presence of an electric field ACSPH105 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - When a charged body moves or is moved from one point to another in an electric field and its potential energy changes, work is done on or by the field





















114 low relevance results shown for 'Electric'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5 | Next | View 100 per page
Showing low relevance matches only. Return to normal search results
Curriculum resources related to 'Electric'
ACSSU097 Year 6 Physical SciencesElectrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU219 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Alternative Energies - Energy from a variety of sources can be used to generate electricity ACSCH030 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - Ions are atoms or groups of atoms that are electrically charged due to an imbalance in the number of electrons and protons; ions are represented by formulae which include the number of constituent atoms and the charge of the ion (for example, O2–, SO42–) ACSCH032 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The characteristic properties of metals (for example, malleability, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity) are explained by modelling metallic bonding as a regular arrangement of positive ions (cations) made stable by electrostatic forces of attra ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSPH016 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Heat transfer occurs between and within systems by conduction, convection and/or radiation ACSPH020 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Provided a substance does not change state, its temperature change is proportional to the amount of energy added to or removed from the substance; the constant of proportionality describes the heat capacity of the substance ACSPH022 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Two systems in contact transfer energy between particles so that eventually the systems reach the same temperature; that is, they are in thermal equilibrium ACSPH028 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Some nuclides are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting alpha, beta and/or gamma radiation over time until they become stable nuclides ACSPH029 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Each species of radionuclide has a specific halflife ACSPH030 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Alpha, beta and gamma radiation have sufficient energy to ionise atoms ACSPH039 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is conserved in the energy transfers and transformations that occur in an electrical circuit ACSPH040 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - The energy available to charges moving in an electrical circuit is measured using electric potential difference, which is defined as the change in potential energy per unit charge between two defined points in the circuit ACSPH041 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is required to separate positive and negative charge carriers; charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that can be used to drive current in circuits ACSPH042 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Power is the rate at which energy is transformed by a circuit component; power enables quantitative analysis of energy transformations in the circuit ACSPH043 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Resistance for ohmic and nonohmic components is defined as the ratio of potential difference across the component to the current in the component ACSPH044 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Circuit analysis and design involve calculation of the potential difference across, the current in, and the power supplied to, components in series, parallel and series/parallel circuits ACSPH137 Year 12 Revolutions in modern physics
Quantum theory - A wide range of phenomena, including black body radiation and the photoelectric effect, are explained using the concept of light quanta ACSPH108 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Magnets, magnetic materials, moving charges and currentcarrying wires experience a force in a magnetic field; this force is utilised in DC electric motors ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system ACSCH031 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The properties of ionic compounds (for example, high melting point, brittleness, ability to conduct electricity when liquid or in solution) are explained by modelling ionic bonding as ions arranged in a crystalline lattice structure with forces of attract ACSCH027 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of atoms - The type of bonding within substances explains their physical properties, including melting and boiling point, conductivity of both electricity and heat, strength and hardness ACSPH103 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - A positively charged body placed in an electric field will experience a force in the direction of the field; the strength of the electric field is defined as the force per unit charge ACSPH104 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Point charges and charged objects produce an electric field in the space that surrounds them; field theory attributes the electrostatic force on a point charge or charged body to the presence of an electric field ACSPH105 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - When a charged body moves or is moved from one point to another in an electric field and its potential energy changes, work is done on or by the field
Products related to 'Electric'

KidWind Solar Energy Exploration Kit
KIDWIND SOLAR ENERGY EXPLORATION KIT
Explore solar energy with this innovative science kit designed to help students investigate energy transformations. A hinged box helps students discover how the angle of photovoltaic panels relative to the sun affects power output. Com...
Order code: KW-SEEK

KidWind SimpleGEN
KIDWIND SIMPLEGEN
The KidWind simpleGEN is an easy-to-build AC generator that allows students to explore the basics of electrical generator design. With the simpleGEN, you can demonstrate Faraday’s law, light LEDs and perform experiments that explore how coils, magnets an...
Order code: KW-SGEN

KidWind SimpleGEN - Classroom Pack
KIDWIND SIMPLEGEN CLASSROOM PACK
The KidWind simpleGEN is an easy-to-build AC generator that allows students to explore the basics of electrical generator design. With the simpleGEN, you can demonstrate Faraday’s law, light LEDs and perform experiments that explore how co...
Order code: KW-SGENC

KidWind Sound And Light Board
KIDWIND SOUND AND LIGHT BOARD
The Sound and Light Board will play music or light LED bulbs with electrical output from a solar panel or small wind turbine.
This is the KidWind simple power output board that comes standard with the KW-MWT
KidWind MINI Wind Turbine. It ...
Order code: KW-SLB

IEC Power Supply 0-500V DC 50mA Digital
IEC 500V DC HIGH VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY DIGITAL
This is a special purpose compact power supply used for electrical experiments requiring smoothed, high voltage DC. The output voltage may be smoothly adjusted from zero to 500V DC or zero to 300V AC at 50mA max total load.
...
Order code: LB2612-002

IEC Power Supply Variable EHV 0-6000V DC
IEC 6000V DC EXTRA HIGH VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY
A special purpose compact power supply used for electrical experiments requiring smoothed, extra high voltage DC. The output voltage may be smoothly adjusted from zero to 6000V DC at no load. As current is drawn from the unit, ...
Order code: LB2615-002
IEC Power Supply 30mA/30V DC
IEC CONSTANT CURRENT POWER SUPPLY
This is a special purpose compact laboratory power supply which may be used for electrical experiments requiring set currents rather than set voltages. A constant current power supply automatically adjusts its output voltage to attempt t...
Order code: LB2618-001

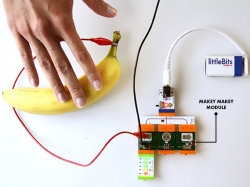
littleBits Makey Makey Module
The LITTLEBITS MAKEY MAKEY MODULE allows you to make a touch-pad out of anything by attaching alligator clip leads to the littleBits Makey Makey module and other objects, for example, you and a banana. When you touch the banana, you complete the connection and the littleBits Make...
Order code: LBMMM

Makey Makey Classic
MAKEY MAKEY CLASSIC
Ever played Mario on modelling clay or piano on bananas? Now you can alligator clip the internet to your world with the Makey Makey Classic.
Makey Makey is an invention kit for the 21st century. Turn everyday objects into touchpads and combine them ...
Order code: MAKEY

IEC Free Fall Mechanical Release 1m without Timer
IEC FREE FALL MECHANICAL RELEASE 1 METRE WITHOUT TIMER
This version of the IEC Free Fall apparatus has a 1m fall and uses a mechanical release for the 3 balls of different sizes and materials. The upper platform is adjustable for position on the 1m vertical rail so that e...
Order code: MF1871-301

IEC Free Fall Mechanical Release 1m with Timer
IEC FREE FALL MECHANICAL RELEASE 1 METRE WITH TIMER
This version of the IEC Free Fall apparatus has a 1m fall and uses a mechanical release for the 3 balls of different sizes and materials. The upper platform is adjustable for position on the 1m vertical rail so that expe...
Order code: MF1871-301A

Vernier Non-Brass Replacement Resistivity Rod Set
VERNIER NON-BRASS REPLACEMENT RESISTIVITY ROD SET.
These four rods have a diameter of about 3.2 mm and are 46 cm long. They replace or supplement the non-brass rods for the Resistivity Set used in our Advanced Physics with Vernier – Beyond Mechanics lab manual.
Use th...
Order code: OT-RRS

IEC Joule's Calorimeter Insert/Stirrer/Element Only
IEC JOULE'S CALORIMETER INSERT WITH STIRRER AND ELEMENT
The insert consists of a black plastic calorimeter lid complete with stirrer and a 2 ohm resistance heating coil connected by metal rods to two 4mm banana plug sockets with spin free heads.
The insert can be place...
Order code: PA0840-002
IEC Electrostatics Graphite In Alcohol 25ml
IEC ELECTROSTATICS GRAPHITE IN ALCOHOL 25ml
25ml bottle of graphite in suspension in alcohol for painting pith balls to make their surface electrically conductive.
Order code: PA1771-010

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 1.2V 250mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 1.2V 250mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 1.2V x 250mA MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-001

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 2.5V 200mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 2.5V 200mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 2.5V x 200mA MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-002

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 3.8V 200mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 3.8V 200mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 3.8V x 200mA MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-003

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 6.2V 150mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 6.2V 150mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 6.2V X 150mA MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-004A

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 6.2V 300/500mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 6.2V 500mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 6.2V X 500mA 3.1W high power MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-005

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 6.0V 200mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 6.0V 200mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 6.0V x 200mA MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-006A

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 6.0V 500mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 6.0V 500mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 6.0V x 500mA 3W high power MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-006B

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 12.0V 100mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 12.0V 100mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 12V 100mA 3W high power MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-007

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 12.0V 500mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 12.0V 500mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 12V x 500mA 6W high power MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-008

IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 1.5V 200mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 1.5V 200mA PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 1.5V x 200mA MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-010
IEC Lamp Torch Bulb MES 2.2V 250mA
IEC LAMP GLOBE MES 2.2V 250mA LENS PACK 10
A pack of 10 general purpose 2.2V x 250mA lens MES (Miniature Edison Screw) light bulbs for electrical experiments.
Order code: PA2040-018
114 low relevance results shown for 'Electric'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5 | Next | View 100 per page



 ,
,