164 results found for 'Red'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7 | Next | View 100 per page
Low relevance matches: 542 other results may be of interest to you. Show low relevance matches
DNA - The transmission of heritable characteristics from one generation to the next involves DNA and genes ACSSU097 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Electrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU115 Year 7 Earth and Space Sciences
Earth Moon Sun - Predictable phenomena on Earth, including seasons and eclipses, are caused by the relative positions of the sun, Earth and the moon ACSSU229 Year 10 Physical Sciences
Forces and Motion - The motion of objects can be described and predicted using the laws of physics ACSBL029 Year 11 Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life
Ecosystem dynamics - Models of ecosystem interactions (for example, food webs, successional models) can be used to predict the impact of change and are based on interpretation of and extrapolation from sample data (for example, data derived from ecosystem surveying techniques ACSBL085 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
DNA genes and the continuity of life - Frequencies of genotypes and phenotypes of offspring can be predicted using probability models, including Punnett squares, and by taking into consideration patterns of inheritance, including the effects of dominant, autosomal and sex-linked alleles and mu ACSBL090 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
Continuity of life on Earth - Natural selection occurs when selection pressures in the environment confer a selective advantage on a specific phenotype to enhance its survival and reproduction; this results in changes in allele frequency in the gene pool of a population ACSBL091 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
Continuity of life on Earth - In additional to environmental selection pressures, mutation, gene flow and genetic drift can contribute to changes in allele frequency in a population gene pool and results in microevolutionary change ACSCH056 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - The shapes of molecules can be explained and predicted using three dimensional representations of electrons as charge clouds and using valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory ACSCH073 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Rates of chemical reactions - Catalysts, including enzymes and metal nanoparticles, affect the rate of certain reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a reduced activation energy, hence increasing the proportion of collisions that lead to a chemical change ACSCH091 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Over time, physical changes and reversible chemical reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium in a closed system, with the relative concentrations of products and reactants defining the position of equilibrium ACSCH096 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Equilibrium position can be predicted qualitatively using equilibrium constants ACSCH097 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acids are substances that can act as proton (hydrogen ion) donors and can be classified as monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of protons donated by each molecule of the acid ACSCH098 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The strength of acids is explained by the degree of ionisation at equilibrium in aqueous solution, which can be represented with chemical equations and equilibrium constants (Ka) ACSCH099 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The relationship between acids and bases in equilibrium systems can be explained using the Brønsted Lowry model and represented using chemical equations that illustrate the transfer of hydrogen ions ACSCH100 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The pH scale is a logarithmic scale and the pH of a solution can be calculated from the concentration of hydrogen ions; Kw can be used to calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions from the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution ACSCH101 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acidbase indicators are weak acids or bases where the acidic form is of a different colour to the basic form ACSCH102 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Volumetric analysis methods involving acidbase reactions rely on the identification of an equivalence point by measuring the associated change in pH, using chemical indicators or pH meters, to reveal an observable end point ACSCH103 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - A range of reactions, including displacement reactions of metals, combustion, corrosion, and electrochemical processes, can be modelled as redox reactions involving oxidation of one substance and reduction of another substance ACSCH104 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Oxidation can be modelled as the loss of electrons from a chemical species, and reduction can be modelled as the gain of electrons by a chemical species; these processes can be represented using half equations ACSCH106 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - The relative strength of oxidising and reducing agents can be determined by comparing standard electrode potentials ACSCH107 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Electrochemical cells, including galvanic and electrolytic cells, consist of oxidation and reduction half reactions connected via an external circuit that allows electrons to move from the anode (oxidation reaction) to the cathode (reduction reaction) ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSCH110 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Cell potentials at standard conditions can be calculated from standard electrode potentials; these values can be used to compare cells constructed from different materials ACSCH130 Year 12 Structure synthesis and design
Properties and structure of organic materials - Data from analytical techniques, including mass spectrometry, xray crystallography and infrared spectroscopy, can be used to determine the structure of organic molecules, often using evidence from more than one technique ACSPH040 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - The energy available to charges moving in an electrical circuit is measured using electric potential difference, which is defined as the change in potential energy per unit charge between two defined points in the circuit ACSPH041 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is required to separate positive and negative charge carriers; charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that can be used to drive current in circuits ACSPH061 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Representations, including graphs and vectors, and/or equations of motion, can be used qualitatively and quantitatively to describe and predict linear motion ACSPH064 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Momentum is a property of moving objects; it is conserved in a closed system and may be transferred from one object to another when a force acts over a time interval ACSPH065 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Energy is conserved in isolated systems and is transferred from one object to another when a force is applied over a distance; this causes work to be done and changes to kinetic and/or potential energy of objects ACSPH073 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A mechanical system resonates when it is driven at one of its natural frequencies of oscillation; energy is transferred efficiently into systems under these conditions ACSPH076 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A wave model explains a wide range of lightrelated phenomena including reflection, refraction, total internal reflection, dispersion, diffraction and interference; a transverse wave model is required to explain polarisation ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system














.jpg)



_Model.jpg)



164 results found for 'Red'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7 | Next | View 100 per page
Low relevance matches: 542 other results may be of interest to you. Show low relevance matches
Curriculum resources related to 'Red'
ACSSU184 Year 10 Biological SciencesDNA - The transmission of heritable characteristics from one generation to the next involves DNA and genes ACSSU097 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Electrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU115 Year 7 Earth and Space Sciences
Earth Moon Sun - Predictable phenomena on Earth, including seasons and eclipses, are caused by the relative positions of the sun, Earth and the moon ACSSU229 Year 10 Physical Sciences
Forces and Motion - The motion of objects can be described and predicted using the laws of physics ACSBL029 Year 11 Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life
Ecosystem dynamics - Models of ecosystem interactions (for example, food webs, successional models) can be used to predict the impact of change and are based on interpretation of and extrapolation from sample data (for example, data derived from ecosystem surveying techniques ACSBL085 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
DNA genes and the continuity of life - Frequencies of genotypes and phenotypes of offspring can be predicted using probability models, including Punnett squares, and by taking into consideration patterns of inheritance, including the effects of dominant, autosomal and sex-linked alleles and mu ACSBL090 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
Continuity of life on Earth - Natural selection occurs when selection pressures in the environment confer a selective advantage on a specific phenotype to enhance its survival and reproduction; this results in changes in allele frequency in the gene pool of a population ACSBL091 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
Continuity of life on Earth - In additional to environmental selection pressures, mutation, gene flow and genetic drift can contribute to changes in allele frequency in a population gene pool and results in microevolutionary change ACSCH056 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - The shapes of molecules can be explained and predicted using three dimensional representations of electrons as charge clouds and using valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory ACSCH073 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Rates of chemical reactions - Catalysts, including enzymes and metal nanoparticles, affect the rate of certain reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a reduced activation energy, hence increasing the proportion of collisions that lead to a chemical change ACSCH091 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Over time, physical changes and reversible chemical reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium in a closed system, with the relative concentrations of products and reactants defining the position of equilibrium ACSCH096 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Equilibrium position can be predicted qualitatively using equilibrium constants ACSCH097 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acids are substances that can act as proton (hydrogen ion) donors and can be classified as monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of protons donated by each molecule of the acid ACSCH098 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The strength of acids is explained by the degree of ionisation at equilibrium in aqueous solution, which can be represented with chemical equations and equilibrium constants (Ka) ACSCH099 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The relationship between acids and bases in equilibrium systems can be explained using the Brønsted Lowry model and represented using chemical equations that illustrate the transfer of hydrogen ions ACSCH100 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The pH scale is a logarithmic scale and the pH of a solution can be calculated from the concentration of hydrogen ions; Kw can be used to calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions from the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution ACSCH101 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acidbase indicators are weak acids or bases where the acidic form is of a different colour to the basic form ACSCH102 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Volumetric analysis methods involving acidbase reactions rely on the identification of an equivalence point by measuring the associated change in pH, using chemical indicators or pH meters, to reveal an observable end point ACSCH103 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - A range of reactions, including displacement reactions of metals, combustion, corrosion, and electrochemical processes, can be modelled as redox reactions involving oxidation of one substance and reduction of another substance ACSCH104 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Oxidation can be modelled as the loss of electrons from a chemical species, and reduction can be modelled as the gain of electrons by a chemical species; these processes can be represented using half equations ACSCH106 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - The relative strength of oxidising and reducing agents can be determined by comparing standard electrode potentials ACSCH107 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Electrochemical cells, including galvanic and electrolytic cells, consist of oxidation and reduction half reactions connected via an external circuit that allows electrons to move from the anode (oxidation reaction) to the cathode (reduction reaction) ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSCH110 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Cell potentials at standard conditions can be calculated from standard electrode potentials; these values can be used to compare cells constructed from different materials ACSCH130 Year 12 Structure synthesis and design
Properties and structure of organic materials - Data from analytical techniques, including mass spectrometry, xray crystallography and infrared spectroscopy, can be used to determine the structure of organic molecules, often using evidence from more than one technique ACSPH040 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - The energy available to charges moving in an electrical circuit is measured using electric potential difference, which is defined as the change in potential energy per unit charge between two defined points in the circuit ACSPH041 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is required to separate positive and negative charge carriers; charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that can be used to drive current in circuits ACSPH061 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Representations, including graphs and vectors, and/or equations of motion, can be used qualitatively and quantitatively to describe and predict linear motion ACSPH064 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Momentum is a property of moving objects; it is conserved in a closed system and may be transferred from one object to another when a force acts over a time interval ACSPH065 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Energy is conserved in isolated systems and is transferred from one object to another when a force is applied over a distance; this causes work to be done and changes to kinetic and/or potential energy of objects ACSPH073 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A mechanical system resonates when it is driven at one of its natural frequencies of oscillation; energy is transferred efficiently into systems under these conditions ACSPH076 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A wave model explains a wide range of lightrelated phenomena including reflection, refraction, total internal reflection, dispersion, diffraction and interference; a transverse wave model is required to explain polarisation ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system
Products related to 'Red'

IEC Digital Voltmeter 200V AC
IEC DIGITAL VOLTMETER 200 Volts AC
An Australian made AC voltmeter designed to be virtually indestructible in the classroom. There are no knobs or fuses to replace.
Powered by an easily changed 9V battery, a "LO BATT" alarm displays well before the battery must be repl...
Order code: LB2126-001

IEC Power Supply Variable EHV 0-6000V DC
IEC 6000V DC EXTRA HIGH VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY
A special purpose compact power supply used for electrical experiments requiring smoothed, extra high voltage DC. The output voltage may be smoothly adjusted from zero to 6000V DC at no load. As current is drawn from the unit, ...
Order code: LB2615-002

IEC Power Supply DIGI PACK 2 to 12V plus 1 to 16V Regulated
IEC POWER SUPPLY 'DIGI PACK'
This double power supply has a standard 2-12V output power supply on the left side of the front panel and a smoothly variable, regulated and filtered 1-16 DC volts, 3 amp output on the right side. Many experiments work well with unfiltered DC ...
Order code: LB2628-001



IEC Power Supply DIGI PAK 2-12V plus 1-16V Regulated
IEC POWER SUPPLY DIGI PAK
The IEC ‘Digi Pak’ power supply is a compact unit with both switched and smoothly adjustable voltages available from a convenient sloping front panel. The green power indicator changes from green to red when the power supply is overloaded.
The...
Order code: LB2628-002

IEC Power Supply Switched General Purpose 2 to 12V AC DC
IEC POWER SUPPLY 2-12V AC/DC 10A WITH OVERLOAD LED
A handy front panel LED indicates when the overload of this model power supply has tripped and reset.
In all other details it is identical to model LB2631-001
This ...
Order code: LB2631-101

IEC Power Supply 0 to 10V DC 10A with Digital Meters
IEC POWER SUPPLY VARIABLE 0-10V DC 10A
This IEC DC Power Supply is suitable for most classroom laboratory experiments where smooth adjustment from zero to 10V DC at about 10 amps maximum. The DC output is full wave rectified but not smoothed.
The digital red LED voltme...
Order code: LB2663-102

IEC Reaction Tester with Decision Function
IEC REACTION TIMER WITH DECISION FUNCTION
The unique IEC Reaction Timer measures the reaction time of a person from when a large LED lights or when a beeper sounds. The large LED can illuminate either red or green. The delay time can be initiated by a second person or by ...
Order code: LB2669-001

IEC Signal Generator - Audio Oscillator 0.1Hz to 99.999kHz 1.5A
IEC MINI-WAVE SIGNAL GENERATOR
The Mini-Wave is a very compact digital, high current instrument with sine, triangular, saw tooth or square wave output.
This signal generator has a broad range that can directly feed a loud speaker, solenoid, vibrator or other electromech...
Order code: LB3753-101


IEC Timer/Counter/Frequency 20 Space Memory 12V
IEC TIMER/COUNTER/FREQUENCY 12V
A versatile, compact and powerful IEC Timer-Counter/Frequency instrument that runs from a 240/12V AC plug pack for general laboratory timing to 0.1mS, counting and measuring frequency or rate. It does not perform Geiger Counting.
With a ...
Order code: LB4063-001
IEC Timer/Counter/Frequency 20 Space Memory 240V
IEC TIMER/COUNTER/FREQUENCY 240V
A versatile, compact and powerful IEC Timer-Counter/Frequency instrument that runs from 240V AC mains power for general laboratory timing to 0.1mS, counting and measuring frequency or rate. It does not perform Geiger Counting.
With a br...
Order code: LB4063-101

IEC Timer LED 6 Digit 999.999Sx0.1ms 12V AC/DC Plug-Pack
IEC MULTI FUNCTION TIMER 12V
This versatile compact low voltage multi function Timer is designed for general purpose timing in the laboratory and and is run by 240/12V AC PlugPak (not supplied). It does not have a power outlet for photogates and it cannot control the IEC ...
Order code: LB4064-001

IEC Multi Timer/Counter/Frequency Meter and Geiger Counter
IEC MULTI TIMER/COUNTER/FREQUENCY/GEIGER
The IEC Multi Counter with frequency, geiger counting and audio amplifier with speaker is the most powerful of all the IEC Timer range. It is 220/240V AC mains operated with a bright red LED display and sloping front panel for ease...
Order code: LB4071-101

Pipette Volumetric A Class 20ml
20ml A Class volumetric pipette +/- 0.030ml, yellow tipped with red 20ml mark.
Order code: LW4124-01

Molymod Amino Acid Set of Seven Models
MOLYMOD AMINO ACID 7 MODEL SET
Use this set of genuine Molymod® atoms to build a model of each of 7 L-configuration amino acids.
Includes a total of 125 atom parts (23mm red oxygen, 23mm blue nitrogen, 23mm black carbon, 23mm yellow sulphur and 19mm white dome hydro...
Order code: MKA-120-7

Molymod Amino Acid Set of 20 Models
MOLYMOD AMINO ACID 20 MODEL SET
Use this set of genuine Molymod® atoms to build a model of each of the 20 common amino acids.
Includes a total of 385 atom parts (23mm red oxygen, 23mm blue nitrogen, 23mm black carbon and 19mm white dome hydrogen) with links (short whi...
Order code: MKA-121-20

Molymod Ice
MOLYMOD ICE
Supplied in a 4 compartment box with illustrated instructions this kit contains sufficient oxygen and hydrogen atoms plus links to build a two layer, 26 water molecule model of ice.
Included are 26 red oxygen atoms, 52 white Hydrogen atoms, 26 grey medium ...
Order code: MKO-123-26
.jpg)
Molymod Calcite Calcium Carbonate
MOLYMOD CALCITE
This model of Calcite or calcium carbonate is supplied pre-assembled and includes 66 atoms:
14 grey metal 6 hole octahedral atoms
13 black carbon 3 hole trigonal planar atoms
39 red oxygen trigonal planar
and required links.
A quality, genuine Molym...
Order code: MKO-126-66
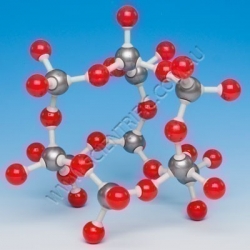
Molymod Quartz
MOLYMOD QUARTZ
Supplied in a four compartment box with illustrated instructions, this kit contains 10 grey silicon atoms, 28 red oxygen atoms and the required links to build the model of silicon dioxide pictured.
A quality, genuine Molymod® product fully compatible w...
Order code: MKO-136-38

Molymod Terylene
MOLYMOD POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE (PET)
A set of genuine Molymod® black carbon, red oxygen and white dome hydrogen atoms,
plus links and a tool to build 2 monomer units into a compact section
of a PET (Terylene) polymer chain.
The approximate inter-nuclear scale...
Order code: MKS-110-2

Molymod Nylon 6.6
MOLYMOD POLYAMIDE (PA) NYLON 6.6
A set of genuine Molymod® black carbon, red oxygen, blue nitrogen and white dome hydrogen atoms,
plus links and a tool to build 2 monomer units into a section of a Polyamide (PA) or Nylon 6.6 condensation polymer chain.
The approxim...
Order code: MKS-111-2

Molymod Soap
MOLYMOD SOAP
A set of genuine Molymod® black carbon, red oxygen, grey sodium and white dome hydrogen atoms,
plus links and a tool to build a model of a soap molecule.
The approximate inter-nuclear scale is 1.45cm/Angstrom
Included:
• 17 x MA-400 black ca...
Order code: MKS-113
_Model.jpg)
Molymod Fat Glyceryl Tristearate
MOLYMOD FAT
A set of genuine Molymod® black carbon, red oxygen, and white dome hydrogen atoms,
plus links and a tool to build one Glyceryl tristearate molecule C57H110O6
The approximate inter-nuclear scale is 1.45cm/Angstrom
I...
Order code: MKS-114

Molymod Glucose 2 Molecules
MOLYMOD GLUCOSE
A set of genuine Molymod® black carbon, red oxygen and white dome hydrogen atoms,
plus links and a tool to build 2 isomeric models of a glucose molecule C6H12O6.
The approximate inter-nuclear scale is 1.45cm/Angstro...
Order code: MKS-115-2

Molymod Model Biochemistry Sucrose
MOLYMOD SUCROSE
A set of genuine Molymod® black carbon, red oxygen and white dome hydrogen atoms,
plus links and a tool to build a model of a sucrose molecule C12H22O11
The approximate inter-nuclear scale is 1.45cm/Angstrom
I...
Order code: MKS-116

Molymod Saturated Fatty Acid Stearic Acid
MOLYMOD STEARIC ACID
A set of genuine Molymod® black carbon, red oxygen and white dome hydrogen atoms,
plus links and a tool to build a compact molecule of Stearic Acid C18H36O2
which is one example of a saturated fatty acid.
The...
Order code: MKS-117-S
164 results found for 'Red'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7 | Next | View 100 per page


