164 results found for 'Red'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7 | Next | View 100 per page
Low relevance matches: 542 other results may be of interest to you. Show low relevance matches
DNA - The transmission of heritable characteristics from one generation to the next involves DNA and genes ACSSU097 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Electrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU115 Year 7 Earth and Space Sciences
Earth Moon Sun - Predictable phenomena on Earth, including seasons and eclipses, are caused by the relative positions of the sun, Earth and the moon ACSSU229 Year 10 Physical Sciences
Forces and Motion - The motion of objects can be described and predicted using the laws of physics ACSBL029 Year 11 Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life
Ecosystem dynamics - Models of ecosystem interactions (for example, food webs, successional models) can be used to predict the impact of change and are based on interpretation of and extrapolation from sample data (for example, data derived from ecosystem surveying techniques ACSBL085 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
DNA genes and the continuity of life - Frequencies of genotypes and phenotypes of offspring can be predicted using probability models, including Punnett squares, and by taking into consideration patterns of inheritance, including the effects of dominant, autosomal and sex-linked alleles and mu ACSBL090 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
Continuity of life on Earth - Natural selection occurs when selection pressures in the environment confer a selective advantage on a specific phenotype to enhance its survival and reproduction; this results in changes in allele frequency in the gene pool of a population ACSBL091 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
Continuity of life on Earth - In additional to environmental selection pressures, mutation, gene flow and genetic drift can contribute to changes in allele frequency in a population gene pool and results in microevolutionary change ACSCH056 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - The shapes of molecules can be explained and predicted using three dimensional representations of electrons as charge clouds and using valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory ACSCH073 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Rates of chemical reactions - Catalysts, including enzymes and metal nanoparticles, affect the rate of certain reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a reduced activation energy, hence increasing the proportion of collisions that lead to a chemical change ACSCH091 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Over time, physical changes and reversible chemical reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium in a closed system, with the relative concentrations of products and reactants defining the position of equilibrium ACSCH096 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Equilibrium position can be predicted qualitatively using equilibrium constants ACSCH097 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acids are substances that can act as proton (hydrogen ion) donors and can be classified as monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of protons donated by each molecule of the acid ACSCH098 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The strength of acids is explained by the degree of ionisation at equilibrium in aqueous solution, which can be represented with chemical equations and equilibrium constants (Ka) ACSCH099 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The relationship between acids and bases in equilibrium systems can be explained using the Brønsted Lowry model and represented using chemical equations that illustrate the transfer of hydrogen ions ACSCH100 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The pH scale is a logarithmic scale and the pH of a solution can be calculated from the concentration of hydrogen ions; Kw can be used to calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions from the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution ACSCH101 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acidbase indicators are weak acids or bases where the acidic form is of a different colour to the basic form ACSCH102 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Volumetric analysis methods involving acidbase reactions rely on the identification of an equivalence point by measuring the associated change in pH, using chemical indicators or pH meters, to reveal an observable end point ACSCH103 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - A range of reactions, including displacement reactions of metals, combustion, corrosion, and electrochemical processes, can be modelled as redox reactions involving oxidation of one substance and reduction of another substance ACSCH104 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Oxidation can be modelled as the loss of electrons from a chemical species, and reduction can be modelled as the gain of electrons by a chemical species; these processes can be represented using half equations ACSCH106 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - The relative strength of oxidising and reducing agents can be determined by comparing standard electrode potentials ACSCH107 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Electrochemical cells, including galvanic and electrolytic cells, consist of oxidation and reduction half reactions connected via an external circuit that allows electrons to move from the anode (oxidation reaction) to the cathode (reduction reaction) ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSCH110 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Cell potentials at standard conditions can be calculated from standard electrode potentials; these values can be used to compare cells constructed from different materials ACSCH130 Year 12 Structure synthesis and design
Properties and structure of organic materials - Data from analytical techniques, including mass spectrometry, xray crystallography and infrared spectroscopy, can be used to determine the structure of organic molecules, often using evidence from more than one technique ACSPH040 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - The energy available to charges moving in an electrical circuit is measured using electric potential difference, which is defined as the change in potential energy per unit charge between two defined points in the circuit ACSPH041 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is required to separate positive and negative charge carriers; charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that can be used to drive current in circuits ACSPH061 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Representations, including graphs and vectors, and/or equations of motion, can be used qualitatively and quantitatively to describe and predict linear motion ACSPH064 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Momentum is a property of moving objects; it is conserved in a closed system and may be transferred from one object to another when a force acts over a time interval ACSPH065 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Energy is conserved in isolated systems and is transferred from one object to another when a force is applied over a distance; this causes work to be done and changes to kinetic and/or potential energy of objects ACSPH073 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A mechanical system resonates when it is driven at one of its natural frequencies of oscillation; energy is transferred efficiently into systems under these conditions ACSPH076 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A wave model explains a wide range of lightrelated phenomena including reflection, refraction, total internal reflection, dispersion, diffraction and interference; a transverse wave model is required to explain polarisation ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system







-head.jpg)
-wm-gizzard.jpg)






164 results found for 'Red'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7 | Next | View 100 per page
Low relevance matches: 542 other results may be of interest to you. Show low relevance matches
Curriculum resources related to 'Red'
ACSSU184 Year 10 Biological SciencesDNA - The transmission of heritable characteristics from one generation to the next involves DNA and genes ACSSU097 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Electrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU115 Year 7 Earth and Space Sciences
Earth Moon Sun - Predictable phenomena on Earth, including seasons and eclipses, are caused by the relative positions of the sun, Earth and the moon ACSSU229 Year 10 Physical Sciences
Forces and Motion - The motion of objects can be described and predicted using the laws of physics ACSBL029 Year 11 Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life
Ecosystem dynamics - Models of ecosystem interactions (for example, food webs, successional models) can be used to predict the impact of change and are based on interpretation of and extrapolation from sample data (for example, data derived from ecosystem surveying techniques ACSBL085 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
DNA genes and the continuity of life - Frequencies of genotypes and phenotypes of offspring can be predicted using probability models, including Punnett squares, and by taking into consideration patterns of inheritance, including the effects of dominant, autosomal and sex-linked alleles and mu ACSBL090 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
Continuity of life on Earth - Natural selection occurs when selection pressures in the environment confer a selective advantage on a specific phenotype to enhance its survival and reproduction; this results in changes in allele frequency in the gene pool of a population ACSBL091 Year 12 Heredity and continuity of life
Continuity of life on Earth - In additional to environmental selection pressures, mutation, gene flow and genetic drift can contribute to changes in allele frequency in a population gene pool and results in microevolutionary change ACSCH056 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - The shapes of molecules can be explained and predicted using three dimensional representations of electrons as charge clouds and using valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory ACSCH073 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Rates of chemical reactions - Catalysts, including enzymes and metal nanoparticles, affect the rate of certain reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a reduced activation energy, hence increasing the proportion of collisions that lead to a chemical change ACSCH091 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Over time, physical changes and reversible chemical reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium in a closed system, with the relative concentrations of products and reactants defining the position of equilibrium ACSCH096 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Equilibrium position can be predicted qualitatively using equilibrium constants ACSCH097 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acids are substances that can act as proton (hydrogen ion) donors and can be classified as monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of protons donated by each molecule of the acid ACSCH098 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The strength of acids is explained by the degree of ionisation at equilibrium in aqueous solution, which can be represented with chemical equations and equilibrium constants (Ka) ACSCH099 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The relationship between acids and bases in equilibrium systems can be explained using the Brønsted Lowry model and represented using chemical equations that illustrate the transfer of hydrogen ions ACSCH100 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The pH scale is a logarithmic scale and the pH of a solution can be calculated from the concentration of hydrogen ions; Kw can be used to calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions from the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution ACSCH101 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acidbase indicators are weak acids or bases where the acidic form is of a different colour to the basic form ACSCH102 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Volumetric analysis methods involving acidbase reactions rely on the identification of an equivalence point by measuring the associated change in pH, using chemical indicators or pH meters, to reveal an observable end point ACSCH103 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - A range of reactions, including displacement reactions of metals, combustion, corrosion, and electrochemical processes, can be modelled as redox reactions involving oxidation of one substance and reduction of another substance ACSCH104 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Oxidation can be modelled as the loss of electrons from a chemical species, and reduction can be modelled as the gain of electrons by a chemical species; these processes can be represented using half equations ACSCH106 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - The relative strength of oxidising and reducing agents can be determined by comparing standard electrode potentials ACSCH107 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Electrochemical cells, including galvanic and electrolytic cells, consist of oxidation and reduction half reactions connected via an external circuit that allows electrons to move from the anode (oxidation reaction) to the cathode (reduction reaction) ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSCH110 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Cell potentials at standard conditions can be calculated from standard electrode potentials; these values can be used to compare cells constructed from different materials ACSCH130 Year 12 Structure synthesis and design
Properties and structure of organic materials - Data from analytical techniques, including mass spectrometry, xray crystallography and infrared spectroscopy, can be used to determine the structure of organic molecules, often using evidence from more than one technique ACSPH040 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - The energy available to charges moving in an electrical circuit is measured using electric potential difference, which is defined as the change in potential energy per unit charge between two defined points in the circuit ACSPH041 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is required to separate positive and negative charge carriers; charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that can be used to drive current in circuits ACSPH061 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Representations, including graphs and vectors, and/or equations of motion, can be used qualitatively and quantitatively to describe and predict linear motion ACSPH064 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Momentum is a property of moving objects; it is conserved in a closed system and may be transferred from one object to another when a force acts over a time interval ACSPH065 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Energy is conserved in isolated systems and is transferred from one object to another when a force is applied over a distance; this causes work to be done and changes to kinetic and/or potential energy of objects ACSPH073 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A mechanical system resonates when it is driven at one of its natural frequencies of oscillation; energy is transferred efficiently into systems under these conditions ACSPH076 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A wave model explains a wide range of lightrelated phenomena including reflection, refraction, total internal reflection, dispersion, diffraction and interference; a transverse wave model is required to explain polarisation ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system
Products related to 'Red'
IEC Wire Nichrome 30 SWG 0.31mm 50g Reel
IEC NICHROME WIRE 30SWG, 0.31mm, 50g
Nichrome resistance wire is an alloy of 80% nickel and 20% chromium used for heating purposes and when the stability of the resistance value is not important.
Nichrome can be run up to very high temperatures where the wire becomes b...
Order code: PA4807-001
IEC Wire Nichrome 32 SWG 0.27mm 50g Reel
IEC NICHROME WIRE 32SWG, 0.27mm, 50g Reel
Nichrome resistance wire is an alloy of 80% nickel and 20% chromium used for heating purposes and when the stability of the resistance value is not important.
Nichrome can be run up to very high temperatures where the wire beco...
Order code: PA4808-001

Infrared Non Contact Thermometer
INFRARED NON CONTACT THERMOMETER.
This handheld IR thermometer has a laser pointer guide and excellent accuracy between -50°C and 580°C. The LCD indicates the measured reading & emissivity value. A new temperature reference mode allows quick verification of ‘within range’...
Order code: SC2235

Infrared Thermometer - High Temperature with K-Type Thermocouple and USB
HIGH TEMPERAUTRE INFRARED THERMOMETER WITH K-TYPE THERMOCOUPLE AND USB.
A professional non-contact thermometer with dual laser sighting to provide fast, easy and accurate readings of most surface temperatures between -50°C to 1650°C.
The impressive 30:1 distance to spot rat...
Order code: SC5037N

Cable Metre Long with Stackable Banana Plugs.
A set of factory moulded piggy back style banana plugs each connected by one metre of high quality 500V DC 12A rated cable. The set contains 2 black, 2 red and one each of blue, yellow and green leads. Seven in all.
Order code: SC5516
| Purchase QTY: (Each) | 1+ |
|---|---|
| Scientrific's price | $44.50 |
| Educational special | $43.90 |
| CLICK FOR QTY PRICING | |
| Prices exclude GST and freight | |
IEC Photo-Electric Cell Base & Terminals with 90CG Tube
PHOTO-ELECTRIC CELL WITH 90CG TUBE
A simple photoelectric cell mounted on a base with terminals for connection to a power source.
The 90CG gas filled photocell runs normally at 90V DC applied to the anode/cathode circuit. The flow of electrons from the cathode to the an...
Order code: AP2330-001

LED Light with Filters for Photosynthesis or Solar Cell Experiments - Mains Powered
A very bright mains powered LED light that is ideal for use with Solar Cells or Photosynthesis experiments with the included 100 x 100 coloured filters.
Durable high-pressure die cast aluminium shell, high-strength tempered glass cover and silicon covers over the charging port...
Order code: SC1127



Brass Reducer for Vacuum Hose
Converts from 12mm I.D. hose as found on older pumps to 6mm as used on our Free Fall Tube, Vacuum Jar, Vacuum Gauge and Shut-Off Valve. Ends are brass hose-tails.
Order code: SC1041

Vernier SparkFun RedBoard with Cable
VERNIER SPARKFUN REDBOARD WITH CABLE
The SparkFun RedBoard is an Arduino-compatible board that is perfect for use with the Vernier Arduino Interface Shield. It is a surface-mount board which is pin-for-pin compatible with a R3 3 Arduino layout. The key difference between ...
Order code: ARD-RED

IEC Air Cored Solenoid 700 Turns
IEC AIR CORED SOLENOID 700 TURNS
The IEC Air Cored Solenoid is a simple solenoid wound with 0.9mm diameter enamelled copper wire on a strong moulded heat resistant plastic bobbin. It contains 700 turns of copper wire and can carry about 5 amps maximum current. The interna...
Order code: EM0090-001


IEC Coil Inductance Air Cored 10MHz
IEC AIR CORED INDUCTANCE COIL 10mH
This yellow coloured coil is the same design and format as the coils supplied with the
EM4089-001 IEC Small Dissectible Transformer and also the
Order code: EM0980-005
IEC Coil Inductance Air Cored 15MHz
IEC AIR CORED INDUCTANCE COIL 15mH
This blue coloured coil is the same design and format as the coils supplied with the
EM4089-001 IEC Small Dissectible Transformer and also the
Order code: EM0980-010
IEC Coil Inductance Air Cored 20MHz
IEC AIR CORED INDUCTANCE COIL 20mH
This green coloured coil is the same design and format as the coils supplied with the
EM4089-001 IEC Small Dissectible Transformer and also the
Order code: EM0980-015

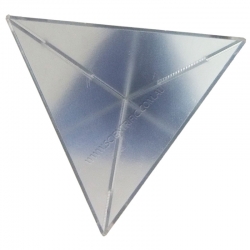
IEC Three Cornered Mirror 120mm Sides
IEC THREE CORNERED MIRROR 120mm SIDES
This special mirror always reflects the incident ray back to the source regardless of the angle of incidence. Three front surfaced mirrors are mounted at 90° to each other inside a plastic moulded housing.
Miniature mirrors of this...
Order code: HL2170-001



Slide Bordered Pits
Last one available
Longitudinal section of a Pinus stem showing bordered pits.
This is a quality Australian made and prepared microscope slide.
Order code: K1624
-head.jpg)
Slide Grasshopper/Cockroach Head Entire Cleared
Last one available
The entire cleared head of a Grasshopper or Cockroach.
This is a quality Australian made and prepared microscope slide.
Order code: K1802
-wm-gizzard.jpg)
Slide Grasshopper/Cockroach Gizzard Portion Flattened and Cleared
Last one available
A flattened and cleared portion of a Grasshopper or Cockroach gizzard.
This is a quality Australian made and prepared microscope slide.
Order code: K1805

IEC Boyles Law High Pressure Coloured Fluid
IEC BOYLES LAW HIGH PRESSURE COLOURED FLUID
A spare bottle of coloured fluid enough for one loading for the MF0360-001P IEC High Pressure Boyle's Law apparatus.
Order code: PA0360-003

Beaker Tongs with plastic covered jaw 240mm long
Beaker Tongs, 240mm long with plastic coated jaws. They open to approximately 130mm.
Order code: SC14121

Infrared Thermometer
INFRARED THERMOMETER. This handheld IR thermometer has a laser guide and excellent accuracy between -50°C and 380°C. The bright backlit LCD shows the scanned temperature, the backlight status (on/off), the laser guide status (on/off) and a low battery warning.
Features:...
Order code: SC4510

Vernier Cable for Infrared Thermometer
VERNIER CABLE FOR INFRARED THERMOMETER
Replacement cable to connect the Vernier Infrared Thermometer to a Vernier interface.
Order code: CB-IRT

Vernier Go Direct ORP Sensor
VERNIER GO DIRECT ORP SENSOR
Vernier's Go Direct ORP (Oxidation-Reduction Potential) Sensor measures the ability of a solution to act as an oxidizing or reducing agent. It directly connects wirelessly via Bluetooth® or wired via USB to your platform.
Use the Vernier Go...
Order code: GDX-ORP

Vernier Go Direct ORP BNC Electrode
VERNIER GO DIRECT ORP BNC ELECTRODE
This is a replacement electrode for GDX-ORP Vernier Go Direct ORP Sensor
The Vernier Go Direct ORP (oxidation-reduction potential) Electrode BNC connects via BNC to Vernier's Go Di...
Order code: GDX-ORP-BNC
164 results found for 'Red'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7 | Next | View 100 per page



