GDX-GPH-BNC electrode only
Enlarge

Requires GDX-EA sold separately
Enlarge

GDX-GPH-BNC electrode only
Enlarge

Requires GDX-EA sold separately
Enlarge
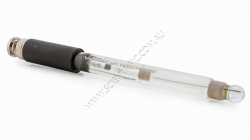
Vernier Go Direct Glass Body pH BNC Electrode
Order code: GDX-GPH-BNC
VERNIER GO DIRECT GLASS BODY pH BNC ELECTRODE
Connect the Glass-Body pH BNC Electrode to Vernier's Go Direct™ Electrode Amplifier to measure pH in aqueous, heterogeneous and organic solutions.
This high-quality glass body pH electrode can be used in non-aqueous solutions and solutions that contain organic solvents, strong acids or strong bases. The electrode features a sealed, gel-filled Ag-AgCl combination reference electrode and uses a BNC connector.
Specifications:
• pH range: 0–14
• Type: Glass shaft, sealed combination electrode with Ag/AgCl reference
• Temperature range: 0–80°C (readings not compensated)
• Accuracy
±0.2 pH units (factory calibration)
±0.05 pH units (user calibration)
• Response time:
2s (to 90% of full reading in aqueous buffer)
5s (to 90% of full reading in 50% acetonitrile)
• Shaft diameter: 12mm OD
• Shaft material: glass
• BNC Connector
Requirements: The Vernier Glass-Body pH Electrode BNC connects via BNC to Vernier's Go Direct Electrode Amplifier or to the discontinued GW-EA Vernier Go Wireless Electrode Amplifier.
Included:
• Vernier Go Direct Glass-Body pH BNC Electrode only
• pH storage solution bottle with pH storage solution
• Electrode tip guard
NOTE: Warranty does not cover accidental breakage of the glass
| User Manual | Vernier Go Direct Glass-Body pH Sensor | ||
Educational use only:
Vernier and Kidwind products are designed for educational use. They are not appropriate for industrial, medical or commercial applications. Details
Warranty
- Warranty: 5 years
Dimensions- Package size (HxWxD): 64x121x235mm
- Packed weight: 160g
Last edited 9th Jan 2025
 This product is used in teaching these Australian Curriculum codes:
This product is used in teaching these Australian Curriculum codes:
ACSSU187 - Chemical Sciences - Chemical Reactions - Different types of chemical reactions are used to produce a range of products and can occur at different rates
ACSBL019 - Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life - Describing biodiversity - Ecosystems are diverse, composed of varied habitats and can be described in terms of their component species, species interactions and the abiotic factors that make up the environment
ACSBL021 - Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life - Describing biodiversity - In addition to biotic factors, abiotic factors including climate and substrate can be used to and classify environments
ACSBL029 - Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life - Ecosystem dynamics - Models of ecosystem interactions (for example, food webs, successional models) can be used to predict the impact of change and are based on interpretation of and extrapolation from sample data (for example, data derived from ecosystem surveying techniques
ACSCH063 - Molecular interactions and reactions - Aqueous solutions and acidity - The concentration of a solution is defined as the amount of solute divided by the amount of solution; this can be represented in a variety of ways including by the number of moles of the solute per litre of solution (mol L1) and the mass of the solute pe
ACSCH066 - Molecular interactions and reactions - Aqueous solutions and acidity - The pH scale is used to compare the levels of acidity or alkalinity of aqueous solutions; the pH is dependent on the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution
ACSCH064 - Molecular interactions and reactions - Aqueous solutions and acidity - The presence of specific ions in solutions can be identified using analytical techniques based on chemical reactions, including precipitation and acidbase reactions
ACSCH097 - Equilibrium acids and redox reactions - Chemical equilibrium systems - Acids are substances that can act as proton (hydrogen ion) donors and can be classified as monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of protons donated by each molecule of the acid
ACSCH096 - Equilibrium acids and redox reactions - Chemical equilibrium systems - Equilibrium position can be predicted qualitatively using equilibrium constants
ACSCH091 - Equilibrium acids and redox reactions - Chemical equilibrium systems - Over time, physical changes and reversible chemical reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium in a closed system, with the relative concentrations of products and reactants defining the position of equilibrium
ACSCH099 - Equilibrium acids and redox reactions - Chemical equilibrium systems - The relationship between acids and bases in equilibrium systems can be explained using the Brønsted Lowry model and represented using chemical equations that illustrate the transfer of hydrogen ions
ACSCH098 - Equilibrium acids and redox reactions - Chemical equilibrium systems - The strength of acids is explained by the degree of ionisation at equilibrium in aqueous solution, which can be represented with chemical equations and equilibrium constants (Ka)
ACSSU176 - Biological Sciences - Ecology - Ecosystems consist of communities of interdependent organisms and abiotic components of the environment; matter and energy flow through these systems
ACSSU179 - Chemical Sciences - Chemical Reactions - Chemical reactions, including combustion and the reactions of acids, are important in both non-living and living systems and involve energy transfer
Click a curriculum code to see other products that relate.
| Works with: | From |
| GDX-PH - Vernier Go Direct pH Sensor | $271.00 |
| GDX-GPH - Vernier Go Direct Glass-Body pH Sensor | $395.00 |
| GDX-EA - Vernier Go Direct Electrode Amplifier | $196.00 |
| PH-SS - Vernier pH Storage Solution | $62.00 |
| Similar Products: | From |
| GDX-GPH - Vernier Go Direct Glass-Body pH Sensor | $395.00 |
| GDX-FPH-BNC - Vernier Go Direct Flat pH BNC Electrode | $206.00 |
| GDX-PH-BNC - Vernier Go Direct pH BNC Electrode | $124.00 |
| GDX-ORP-BNC - Vernier Go Direct ORP BNC Electrode | $147.00 |
| GDX-NO3-BNC - Vernier Go Direct Nitrate Ion-Selective Electrode BNC | $650.00 |
| GDX-NH4-BNC - Vernier Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode BNC | $650.00 |
| GDX-K-BNC - Vernier Go Direct Potassium Ion-Selective Electrode BNC | $619.00 |
| GDX-CA-BNC - Vernier Go Direct Calcium Ion-Selective Electrode BNC | $619.00 |
| GDX-CL-BNC - Vernier Go Direct Chloride Ion-Selective Electrode BNC | $619.00 |
| GPH-BNC - Vernier Glass Body pH Electrode BNC | $248.00 |
Documents: Catalogue | Vernier Catalogue K-12 | Catalogue | Vernier Catalogue Uni | Catalogue | Scientrific April 2025 Mini Catalogue | Catalogue | Vernier 2025 K-12 Catalogue | Catalogue | Vernier 2025 University Catalogue | Compatibility Guide | Sensor-Interface-Software Requirements (external link) | User Manual | Vernier Go Direct Glass-Body pH Sensor | | |||||||||||||||
Note: Prices do NOT include GST or freight


