37 low relevance results shown for 'acid'. |1|2 | Next | View 100 per page
Showing low relevance matches only. Return to normal search results
Chemical Reactions - Chemical reactions, including combustion and the reactions of acids, are important in both non-living and living systems and involve energy transfer ACSCH061 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - Water is a key substance in a range of chemical systems because of its unique properties, including its boiling point, density in solid and liquid phases, surface tension, and ability to act as a solvent ACSCH063 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The concentration of a solution is defined as the amount of solute divided by the amount of solution; this can be represented in a variety of ways including by the number of moles of the solute per litre of solution (mol L1) and the mass of the solute pe ACSCH064 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The presence of specific ions in solutions can be identified using analytical techniques based on chemical reactions, including precipitation and acidbase reactions ACSCH065 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The solubility of substances in water, including ionic and molecular substances, can be explained by the intermolecular forces between species in the substances and water molecules, and is affected by changes in temperature ACSCH066 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The pH scale is used to compare the levels of acidity or alkalinity of aqueous solutions; the pH is dependent on the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution ACSCH091 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Over time, physical changes and reversible chemical reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium in a closed system, with the relative concentrations of products and reactants defining the position of equilibrium ACSCH096 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Equilibrium position can be predicted qualitatively using equilibrium constants ACSCH097 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acids are substances that can act as proton (hydrogen ion) donors and can be classified as monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of protons donated by each molecule of the acid ACSCH098 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The strength of acids is explained by the degree of ionisation at equilibrium in aqueous solution, which can be represented with chemical equations and equilibrium constants (Ka) ACSCH099 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The relationship between acids and bases in equilibrium systems can be explained using the Brønsted Lowry model and represented using chemical equations that illustrate the transfer of hydrogen ions ACSCH100 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The pH scale is a logarithmic scale and the pH of a solution can be calculated from the concentration of hydrogen ions; Kw can be used to calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions from the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution ACSCH101 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acidbase indicators are weak acids or bases where the acidic form is of a different colour to the basic form ACSCH102 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Volumetric analysis methods involving acidbase reactions rely on the identification of an equivalence point by measuring the associated change in pH, using chemical indicators or pH meters, to reveal an observable end point ACSCH103 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - A range of reactions, including displacement reactions of metals, combustion, corrosion, and electrochemical processes, can be modelled as redox reactions involving oxidation of one substance and reduction of another substance ACSCH104 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Oxidation can be modelled as the loss of electrons from a chemical species, and reduction can be modelled as the gain of electrons by a chemical species; these processes can be represented using half equations ACSCH106 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - The relative strength of oxidising and reducing agents can be determined by comparing standard electrode potentials ACSCH107 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Electrochemical cells, including galvanic and electrolytic cells, consist of oxidation and reduction half reactions connected via an external circuit that allows electrons to move from the anode (oxidation reaction) to the cathode (reduction reaction) ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSCH110 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Cell potentials at standard conditions can be calculated from standard electrode potentials; these values can be used to compare cells constructed from different materials























37 low relevance results shown for 'acid'. |1|2 | Next | View 100 per page
Showing low relevance matches only. Return to normal search results
Curriculum resources related to 'acid'
ACSSU179 Year 9 Chemical SciencesChemical Reactions - Chemical reactions, including combustion and the reactions of acids, are important in both non-living and living systems and involve energy transfer ACSCH061 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - Water is a key substance in a range of chemical systems because of its unique properties, including its boiling point, density in solid and liquid phases, surface tension, and ability to act as a solvent ACSCH063 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The concentration of a solution is defined as the amount of solute divided by the amount of solution; this can be represented in a variety of ways including by the number of moles of the solute per litre of solution (mol L1) and the mass of the solute pe ACSCH064 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The presence of specific ions in solutions can be identified using analytical techniques based on chemical reactions, including precipitation and acidbase reactions ACSCH065 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The solubility of substances in water, including ionic and molecular substances, can be explained by the intermolecular forces between species in the substances and water molecules, and is affected by changes in temperature ACSCH066 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The pH scale is used to compare the levels of acidity or alkalinity of aqueous solutions; the pH is dependent on the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution ACSCH091 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Over time, physical changes and reversible chemical reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium in a closed system, with the relative concentrations of products and reactants defining the position of equilibrium ACSCH096 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Equilibrium position can be predicted qualitatively using equilibrium constants ACSCH097 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acids are substances that can act as proton (hydrogen ion) donors and can be classified as monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of protons donated by each molecule of the acid ACSCH098 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The strength of acids is explained by the degree of ionisation at equilibrium in aqueous solution, which can be represented with chemical equations and equilibrium constants (Ka) ACSCH099 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The relationship between acids and bases in equilibrium systems can be explained using the Brønsted Lowry model and represented using chemical equations that illustrate the transfer of hydrogen ions ACSCH100 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - The pH scale is a logarithmic scale and the pH of a solution can be calculated from the concentration of hydrogen ions; Kw can be used to calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions from the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution ACSCH101 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acidbase indicators are weak acids or bases where the acidic form is of a different colour to the basic form ACSCH102 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Volumetric analysis methods involving acidbase reactions rely on the identification of an equivalence point by measuring the associated change in pH, using chemical indicators or pH meters, to reveal an observable end point ACSCH103 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - A range of reactions, including displacement reactions of metals, combustion, corrosion, and electrochemical processes, can be modelled as redox reactions involving oxidation of one substance and reduction of another substance ACSCH104 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Oxidation can be modelled as the loss of electrons from a chemical species, and reduction can be modelled as the gain of electrons by a chemical species; these processes can be represented using half equations ACSCH106 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - The relative strength of oxidising and reducing agents can be determined by comparing standard electrode potentials ACSCH107 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Electrochemical cells, including galvanic and electrolytic cells, consist of oxidation and reduction half reactions connected via an external circuit that allows electrons to move from the anode (oxidation reaction) to the cathode (reduction reaction) ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSCH110 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Cell potentials at standard conditions can be calculated from standard electrode potentials; these values can be used to compare cells constructed from different materials
Products related to 'acid'

Nalgene Amber Narrow Mouth Bottle HDPE 30ml
A Nalgene branded narrow mouthed round 30 ml bottle made of amber high density polyethylene with a 20 mm amber polypropylene screw closure.
Features:
Reduce UV light transmission to help protect light sensitive liquids.
Nalgene amber bottles comply with U.S. Pharmacop...
Order code: 2004-0001

Nalgene Amber Narrow Mouth Bottle HDPE 60ml
A Nalgene branded narrow mouthed round 60 ml bottle made of amber high density polyethylene with a 20 mm amber polypropylene screw closure.
Features:
Reduce UV light transmission to help protect light sensitive liquids.
Nalgene amber bottles comply with U.S. Pharmacop...
Order code: 2004-0002

Vernier Go Direct Wide Range Temperature Probe
VERNIER GO DIRECT WIDE RANGE TEMPERATURE PROBE
Measuring the temperature of a distillation has never been safer — your students can conduct an experiment within the laboratory fume hood while collecting data at their lab station. The Vernier Go Direct Wide-Range Temperatu...
Order code: GDX-WRT

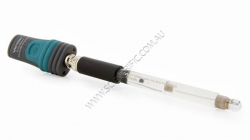
Vernier Go Direct pH Sensor
VERNIER GO DIRECT pH SENSOR
Vernier's Go Direct pH Sensor is a general purpose pH sensor used to monitor the pH of aqueous solutions. It directly connects wirelessly via Bluetooth® or wired via USB to your platform.
The Vernier Go Direct pH Sensor is an important and v...
Order code: GDX-PH

Vernier Go Direct Polarimeter
VERNIER GO DIRECT POLARIMETER
The concept of chirality can be difficult for students to visualize. Vernier's Go Direct Polarimeter provides a visual representation of this concept by measuring the optical rotation of optical isomers such as sugars, amino acids and protein...
Order code: GDX-POL

Vernier Stainless Steel Temperature Probe
VERNIER STAINLESS STEEL TEMPERATURE PROBE
Vernier's Stainless Steel Temperature Probe is a rugged, general-purpose temperature sensor with a sealed stainless steel shaft and tip that can be used in organic liquids, salt solutions, acids and bases. Use it as you would use ...
Order code: TMP-BTA

Vernier Go Direct Conductivity Probe
VERNIER GO DIRECT CONDUCTIVITY PROBE
Vernier's Go Direct Conductivity Probe determines the ionic content of an aqueous solution by measuring its electrical conductivity. It directly connects wirelessly via Bluetooth® or wired via USB to your platform.
The Vernier Go Di...
Order code: GDX-CON

Vernier Go Direct Drop Counter
VERNIER GO DIRECT DROP COUNTER
Vernier's Go Direct Drop Counter precisely records the number of drops of titrant added during a titration and then automatically converts it to volume. It directly connects wirelessly via Bluetooth® or wired via USB to your platform.
Con...
Order code: GDX-DC

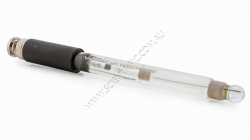
Vernier Go Direct Glass-Body pH Sensor
VERNIER GO DIRECT GLASS BODY pH SENSOR
This high-quality glass body pH sensor can be used in non-aqueous solutions and solutions that contain organic solvents, strong acids or strong bases. The electrode features a sealed, gel-filled Ag-AgCl combination reference electrod...
Order code: GDX-GPH

Vernier Go Direct Platinum-Cell Conductivity Probe
VERNIER GO DIRECT PLATINUM-CELL CONDUCTIVITY PROBE
Perfect for senior secondary and university general chemistry, Vernier's Go Direct Platinum-Cell Conductivity Probe provides an accurate and easy measurement of a solution’s conductivity or its total ion concentration. Th...
Order code: GDX-CONPT

Vernier Go Direct pH Teacher Pack
VERNIER GO DIRECT pH SENSOR TEACHER PACK
Buy more and save. With Vernier's Go Direct pH Teacher Pack you receive eight Go Direct pH Sensors and the convenient Vernier Go Direct Charging Station that allows you to charge eight Vernier Go Direct pH Sensors at a time.
The...
Order code: GDX-PH-TP

Vernier Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode
VERNIER GO DIRECT AMMONIUM ION-SELECTIVE ELECTRODE
Vernier's Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) can be used to measure the concentration of ammonium (NH4+) in aqueous samples. It connects via Bluetooth® wireless technology or wired via USB to your device.
...
Order code: GDX-NH4

Vernier Go Direct Nitrate Ion-Selective Electrode
VERNIER GO DIRECT NITRATE ION-SELECTIVE ELECTRODE
The Vernier Go Direct Nitrate Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) can be used to measure the concentration of nitrate (NO3-) in aqueous samples. It connects via Bluetooth® wireless technology or wired via USB to your device.
...
Order code: GDX-NO3

Vernier Go Direct Glass Body pH BNC Electrode
VERNIER GO DIRECT GLASS BODY pH BNC ELECTRODE
Connect the Glass-Body pH BNC Electrode to Vernier's Go Direct™ Electrode Amplifier to measure pH in aqueous, heterogeneous and organic solutions.
This high-quality glass body pH electrode can be used in non-aqueous solutio...
Order code: GDX-GPH-BNC

Vernier Conductivity Probe
VERNIER CONDUCTIVITY PROBE
The Vernier Conductivity Probe determines the ionic content of an aqueous solution by measuring its conductivity. This has many applications in chemistry, biology and environmental science.
Vernier's conductivity probe has three ranges provid...
Order code: CON-BTA

Vernier Go Direct Chemistry Package For ADILT
VERNIER GO DIRECT CHEMISTRY PACKAGE FOR ADLIT
AD Instruments online Lt Chemistry course collection, developed in partnership with Vernier, covers core concepts in first year university chemistry courses. The collection introduces a variety of concepts fundamental to chemi...
Order code: CHEMPKG-ADILT

Vernier Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode
VERNIER AMMONIUM ION-SELECTIVE ELECTRODE
Vernier's Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) can be used to measure the concentration of ammonium (NH4+) in aqueous samples.
Use the Vernier Ammonium ISE to measure levels of ammonium ions introduced from fertilizers. It can...
Order code: NH4-BTA

Vernier Nitrate Ion-Selective Electrode
VERNIER NITRATE ION-SELECTIVE ELECTRODE
Vernier's Nitrate Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) can be used to measure the concentration of Nitrate (NO3-) in aqueous samples.
Nitrate concentration, which can be increased by acidic rainfall, fertilizer runoff from fields and pl...
Order code: NO3-BTA

Vernier Wide Range Temperature Probe
VERNIER WIDE RANGE TEMPERATURE PROBE
Vernier's rugged Wide-Range Temperature Probe measures a wide temperature range from –20 to 330°C. The high upper limit of the sensor allows melting point determinations of most organic compounds. It uses Resistance Temperature Detecti...
Order code: WRT-BTA

Vernier Plastic 2-Way Valve
VERNIER PLASTIC 2-WAY VALVE
A replacement plastic stopcock with Luer-Lock connections for the VDC-BTD Vernier Drop Counter and the PS-ACC Vernier Pressure Sensor Accessories Kit.
The body is polycarbonate and the handle is high density polyethylene. Chemical resistanc...
Order code: PS-2WAY

Advanced Chemistry with Vernier
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY WITH VERNIER
Advanced Chemistry with Vernier is a lab book containing 35 advanced chemistry experiments designed for use with Vernier data-collection technology. There are four student alternative versions included for each experiment: Logger Pro, LabQu...
Order code: CHEM-A

Advanced Chemistry with Vernier - Electronic Version
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY WITH VERNIER - ELECTRONIC
Advanced Chemistry with Vernier is a lab book containing 35 advanced chemistry experiments designed for use with Vernier data-collection technology. There are four student alternative versions included for each experiment: Logg...
Order code: CHEM-A-E

Vernier Food Chemistry Experiments
Vernier Food Chemistry Experiments
Vernier Food Chemistry Experiments has 14 experiments that use food as a means to explore crucial chemistry concepts. Students are more likely to engage with science when they see concepts applied to the real world. These experiments use...
Order code: HSB-FOOD

Vernier Food Chemistry Experiments E-Book
VERNIER FOOD CHEMISTRY EXPERIMENTS E-BOOK
Vernier Food Chemistry Experiments e-book has 14 experiments that use food as a means to explore crucial chemistry concepts. Students are more likely to engage with science when they see concepts applied to the real world. These e...
Order code: HSB-FOOD-E

Vernier Exploring Chemical Reactions - E Version
VERNIER EXPLORING CHEMICAL REACTIONS EBOOK
Explore various types of chemical reactions with your Years 4-8 Middle School students as they build a model to explain what goes on at the molecular level during a chemical reaction. Students investigate endothermic and exotherm...
Order code: MSB-CR-E
37 low relevance results shown for 'acid'. |1|2 | Next | View 100 per page



 ,
,