424 low relevance results shown for 'for'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9|10|11|12|13|14|15|16|17 | Next | View 100 per page
Showing low relevance matches only. Return to normal search results
Forces and Moving - The way objects move depends on a variety of factors including their size and shape ACSSU031 Year 2 Chemical Sciences
Materials - Different materials can be combined, including by mixing, for a particular purpose ACSSU033 Year 2 Physical Sciences
Forces and Moving - A push or a pull affects how an object moves or changes shape ACSSU076 Year 4 Physical Sciences
Forces and Moving - Forces can be exerted by one object on another through direct contact or from a distance ACSSU080 Year 5 Physical Sciences
Light and Sound - Light from a source forms shadows and can be absorbed, reflected and refracted ACSSU097 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Electrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU117 Year 7 Physical Sciences
Forces and Machines - Change to an object’s motion is caused by unbalanced forces, including Earth’s gravitational attraction, acting on the object ACSSU153 Year 8 Earth and Space Sciences
Rocks and Minerals - Sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks contain minerals and are formed by processes that occur within Earth over a variety of timescales ACSSU155 Year 8 Physical Sciences
Energy Forms - Energy appears in different forms, including movement (kinetic energy), heat and potential energy, and energy transformations and transfers cause change within systems ACSSU178 Year 9 Chemical Sciences
Chemical Reactions - Chemical reactions involve rearranging atoms to form new substances; during a chemical reaction mass is not created or destroyed ACSSU225 Year 8 Chemical Sciences
Chemical Reactions - Chemical change involves substances reacting to form new substances ACSSU190 Year 10 Physical Sciences
Energy Conservation - Energy conservation in a system can be explained by describing energy transfers and transformations ACSSU229 Year 10 Physical Sciences
Forces and Motion - The motion of objects can be described and predicted using the laws of physics ACSBL029 Year 11 Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life
Ecosystem dynamics - Models of ecosystem interactions (for example, food webs, successional models) can be used to predict the impact of change and are based on interpretation of and extrapolation from sample data (for example, data derived from ecosystem surveying techniques ACSBL115 Year 12 Maintaining the internal environment
Homeostasis - Animals, whether osmo-regulators or osmo-conformers, and plants, have various mechanisms to maintain water balance that involve structural features, and behavioural, physiological and homeostatic responses ACSCH018 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of atoms - Atoms can be modelled as a nucleus surrounded by electrons in distinct energy levels, held together by electrostatic forces of attraction between the nucleus and electrons; atoms can be represented using electron shell diagrams (all electron shells or val ACSCH025 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - Materials are either pure substances with distinct measurable properties (for example, melting and boiling point, reactivity, strength, density) or mixtures with properties dependent on the identity and relative amounts of the substances that make up the ACSCH030 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - Ions are atoms or groups of atoms that are electrically charged due to an imbalance in the number of electrons and protons; ions are represented by formulae which include the number of constituent atoms and the charge of the ion (for example, O2–, SO42–) ACSCH032 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The characteristic properties of metals (for example, malleability, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity) are explained by modelling metallic bonding as a regular arrangement of positive ions (cations) made stable by electrostatic forces of attra ACSCH036 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Chemical reactions - All chemical reactions involve the creation of new substances and associated energy transformations, commonly observable as changes in the temperature of the surroundings and/or the emission of light ACSCH037 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Chemical reactions - Endothermic and exothermic reactions can be explained in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy and the breaking and reforming of bonds; heat energy released or absorbed can be represented in thermochemical equations ACSCH039 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Chemical reactions - A mole is a precisely defined quantity of matter equal to Avogadro’s number of particles; the mole concept and the Law of Conservation of Mass can be used to calculate the mass of reactants and products in a chemical reaction ACSCH056 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - The shapes of molecules can be explained and predicted using three dimensional representations of electrons as charge clouds and using valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory ACSCH059 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - Data from chromatography techniques (for example, thin layer, gas and highperformance liquid chromatography) can be used to determine the composition and purity of substances; the separation of the components is caused by the variation of strength of the ACSCH060 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - The behaviour of gases, including the qualitative relationships between pressure, temperature and volume, can be explained using kinetic theory ACSCH065 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The solubility of substances in water, including ionic and molecular substances, can be explained by the intermolecular forces between species in the substances and water molecules, and is affected by changes in temperature ACSCH069 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Rates of chemical reactions - The rate of chemical reactions can be quantified by measuring the rate of formation of products or the depletion of reactants ACSCH101 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acidbase indicators are weak acids or bases where the acidic form is of a different colour to the basic form ACSCH131 Year 12 Structure synthesis and design
Chemical synthesis and design - Chemical synthesis involves the selection of particular reagents to form a product with specific properties (for example, pharmaceuticals, fuels, cosmetics, cleaning products) ACSPH039 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is conserved in the energy transfers and transformations that occur in an electrical circuit ACSPH042 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Power is the rate at which energy is transformed by a circuit component; power enables quantitative analysis of energy transformations in the circuit ACSPH043 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Resistance for ohmic and nonohmic components is defined as the ratio of potential difference across the component to the current in the component ACSPH060 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Uniformly accelerated motion is described in terms of relationships between measurable scalar and vector quantities, including displacement, speed, velocity and acceleration ACSPH061 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Representations, including graphs and vectors, and/or equations of motion, can be used qualitatively and quantitatively to describe and predict linear motion ACSPH062 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Vertical motion is analysed by assuming the acceleration due to gravity is constant near Earth’s surface ACSPH063 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Newton’s Three Laws of Motion describe the relationship between the force or forces acting on an object, modelled as a point mass, and the motion of the object due to the application of the force or forces ACSPH064 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Momentum is a property of moving objects; it is conserved in a closed system and may be transferred from one object to another when a force acts over a time interval ACSPH065 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Energy is conserved in isolated systems and is transferred from one object to another when a force is applied over a distance; this causes work to be done and changes to kinetic and/or potential energy of objects ACSPH066 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Collisions may be elastic and inelastic; kinetic energy is conserved in elastic collisions ACSPH072 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - The superposition of waves in a medium may lead to the formation of standing waves and interference phenomena, including standing waves in pipes and on stretched strings ACSPH102 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Electrostatically charged objects exert a force upon one another; the magnitude of this force can be calculated using Coulomb’s Law ACSPH110 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - A changing magnetic flux induces a potential difference; this process of electromagnetic induction is used in stepup and stepdown transformers, DC and AC generators, and AC induction motors ACSBL053 Year 11 Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life
Ecosystem dynamics - Cellular respiration is a biochemical process that occurs in different locations in the cytosol and mitochondria and metabolises organic compounds, aerobically or anaerobically, to release useable energy in the form of ATP; the overall process can be repr ACSPH108 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Magnets, magnetic materials, moving charges and currentcarrying wires experience a force in a magnetic field; this force is utilised in DC electric motors ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system ACSPH100 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Gravity and motion - When an object experiences a net force of constant magnitude perpendicular to its velocity, it will undergo uniform circular motion, including circular motion on a horizontal plane and around a banked track ACSCH031 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The properties of ionic compounds (for example, high melting point, brittleness, ability to conduct electricity when liquid or in solution) are explained by modelling ionic bonding as ions arranged in a crystalline lattice structure with forces of attract ACSCH137 Year 12 Structure synthesis and design
Chemical synthesis and design - Fuels (for example, biodiesel, ethanol, hydrogen) can be synthesised from organic or inorganic sources using a range of chemical reactions including addition, oxidation and esterification ACSPH075 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A ray model of light may be used to describe reflection, refraction and image formation from lenses and mirrors ACSPH077 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - The speed of light is finite and many orders of magnitude greater than the speed of mechanical waves (for example, sound and water waves); its intensity decreases in an inverse square relationship with distance from a point source ACSPH098 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Gravity and motion - The vector nature of the gravitational force can be used to analyse motion on inclined planes by considering the components of the gravitational force (that is, weight) parallel and perpendicular to the plane ACSPH103 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - A positively charged body placed in an electric field will experience a force in the direction of the field; the strength of the electric field is defined as the force per unit charge ACSPH104 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Point charges and charged objects produce an electric field in the space that surrounds them; field theory attributes the electrostatic force on a point charge or charged body to the presence of an electric field ACSPH105 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - When a charged body moves or is moved from one point to another in an electric field and its potential energy changes, work is done on or by the field




















424 low relevance results shown for 'for'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9|10|11|12|13|14|15|16|17 | Next | View 100 per page
Showing low relevance matches only. Return to normal search results
Curriculum resources related to 'for'
ACSSU005 Foundation Physical SciencesForces and Moving - The way objects move depends on a variety of factors including their size and shape ACSSU031 Year 2 Chemical Sciences
Materials - Different materials can be combined, including by mixing, for a particular purpose ACSSU033 Year 2 Physical Sciences
Forces and Moving - A push or a pull affects how an object moves or changes shape ACSSU076 Year 4 Physical Sciences
Forces and Moving - Forces can be exerted by one object on another through direct contact or from a distance ACSSU080 Year 5 Physical Sciences
Light and Sound - Light from a source forms shadows and can be absorbed, reflected and refracted ACSSU097 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Electrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU117 Year 7 Physical Sciences
Forces and Machines - Change to an object’s motion is caused by unbalanced forces, including Earth’s gravitational attraction, acting on the object ACSSU153 Year 8 Earth and Space Sciences
Rocks and Minerals - Sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks contain minerals and are formed by processes that occur within Earth over a variety of timescales ACSSU155 Year 8 Physical Sciences
Energy Forms - Energy appears in different forms, including movement (kinetic energy), heat and potential energy, and energy transformations and transfers cause change within systems ACSSU178 Year 9 Chemical Sciences
Chemical Reactions - Chemical reactions involve rearranging atoms to form new substances; during a chemical reaction mass is not created or destroyed ACSSU225 Year 8 Chemical Sciences
Chemical Reactions - Chemical change involves substances reacting to form new substances ACSSU190 Year 10 Physical Sciences
Energy Conservation - Energy conservation in a system can be explained by describing energy transfers and transformations ACSSU229 Year 10 Physical Sciences
Forces and Motion - The motion of objects can be described and predicted using the laws of physics ACSBL029 Year 11 Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life
Ecosystem dynamics - Models of ecosystem interactions (for example, food webs, successional models) can be used to predict the impact of change and are based on interpretation of and extrapolation from sample data (for example, data derived from ecosystem surveying techniques ACSBL115 Year 12 Maintaining the internal environment
Homeostasis - Animals, whether osmo-regulators or osmo-conformers, and plants, have various mechanisms to maintain water balance that involve structural features, and behavioural, physiological and homeostatic responses ACSCH018 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of atoms - Atoms can be modelled as a nucleus surrounded by electrons in distinct energy levels, held together by electrostatic forces of attraction between the nucleus and electrons; atoms can be represented using electron shell diagrams (all electron shells or val ACSCH025 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - Materials are either pure substances with distinct measurable properties (for example, melting and boiling point, reactivity, strength, density) or mixtures with properties dependent on the identity and relative amounts of the substances that make up the ACSCH030 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - Ions are atoms or groups of atoms that are electrically charged due to an imbalance in the number of electrons and protons; ions are represented by formulae which include the number of constituent atoms and the charge of the ion (for example, O2–, SO42–) ACSCH032 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The characteristic properties of metals (for example, malleability, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity) are explained by modelling metallic bonding as a regular arrangement of positive ions (cations) made stable by electrostatic forces of attra ACSCH036 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Chemical reactions - All chemical reactions involve the creation of new substances and associated energy transformations, commonly observable as changes in the temperature of the surroundings and/or the emission of light ACSCH037 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Chemical reactions - Endothermic and exothermic reactions can be explained in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy and the breaking and reforming of bonds; heat energy released or absorbed can be represented in thermochemical equations ACSCH039 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Chemical reactions - A mole is a precisely defined quantity of matter equal to Avogadro’s number of particles; the mole concept and the Law of Conservation of Mass can be used to calculate the mass of reactants and products in a chemical reaction ACSCH056 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - The shapes of molecules can be explained and predicted using three dimensional representations of electrons as charge clouds and using valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory ACSCH059 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - Data from chromatography techniques (for example, thin layer, gas and highperformance liquid chromatography) can be used to determine the composition and purity of substances; the separation of the components is caused by the variation of strength of the ACSCH060 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Intermolecular forces and gases - The behaviour of gases, including the qualitative relationships between pressure, temperature and volume, can be explained using kinetic theory ACSCH065 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Aqueous solutions and acidity - The solubility of substances in water, including ionic and molecular substances, can be explained by the intermolecular forces between species in the substances and water molecules, and is affected by changes in temperature ACSCH069 Year 11 Molecular interactions and reactions
Rates of chemical reactions - The rate of chemical reactions can be quantified by measuring the rate of formation of products or the depletion of reactants ACSCH101 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Chemical equilibrium systems - Acidbase indicators are weak acids or bases where the acidic form is of a different colour to the basic form ACSCH131 Year 12 Structure synthesis and design
Chemical synthesis and design - Chemical synthesis involves the selection of particular reagents to form a product with specific properties (for example, pharmaceuticals, fuels, cosmetics, cleaning products) ACSPH039 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is conserved in the energy transfers and transformations that occur in an electrical circuit ACSPH042 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Power is the rate at which energy is transformed by a circuit component; power enables quantitative analysis of energy transformations in the circuit ACSPH043 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Resistance for ohmic and nonohmic components is defined as the ratio of potential difference across the component to the current in the component ACSPH060 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Uniformly accelerated motion is described in terms of relationships between measurable scalar and vector quantities, including displacement, speed, velocity and acceleration ACSPH061 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Representations, including graphs and vectors, and/or equations of motion, can be used qualitatively and quantitatively to describe and predict linear motion ACSPH062 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Vertical motion is analysed by assuming the acceleration due to gravity is constant near Earth’s surface ACSPH063 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Newton’s Three Laws of Motion describe the relationship between the force or forces acting on an object, modelled as a point mass, and the motion of the object due to the application of the force or forces ACSPH064 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Momentum is a property of moving objects; it is conserved in a closed system and may be transferred from one object to another when a force acts over a time interval ACSPH065 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Energy is conserved in isolated systems and is transferred from one object to another when a force is applied over a distance; this causes work to be done and changes to kinetic and/or potential energy of objects ACSPH066 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Linear motion and force - Collisions may be elastic and inelastic; kinetic energy is conserved in elastic collisions ACSPH072 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - The superposition of waves in a medium may lead to the formation of standing waves and interference phenomena, including standing waves in pipes and on stretched strings ACSPH102 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Electrostatically charged objects exert a force upon one another; the magnitude of this force can be calculated using Coulomb’s Law ACSPH110 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - A changing magnetic flux induces a potential difference; this process of electromagnetic induction is used in stepup and stepdown transformers, DC and AC generators, and AC induction motors ACSBL053 Year 11 Biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life
Ecosystem dynamics - Cellular respiration is a biochemical process that occurs in different locations in the cytosol and mitochondria and metabolises organic compounds, aerobically or anaerobically, to release useable energy in the form of ATP; the overall process can be repr ACSPH108 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Magnets, magnetic materials, moving charges and currentcarrying wires experience a force in a magnetic field; this force is utilised in DC electric motors ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system ACSPH100 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Gravity and motion - When an object experiences a net force of constant magnitude perpendicular to its velocity, it will undergo uniform circular motion, including circular motion on a horizontal plane and around a banked track ACSCH031 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The properties of ionic compounds (for example, high melting point, brittleness, ability to conduct electricity when liquid or in solution) are explained by modelling ionic bonding as ions arranged in a crystalline lattice structure with forces of attract ACSCH137 Year 12 Structure synthesis and design
Chemical synthesis and design - Fuels (for example, biodiesel, ethanol, hydrogen) can be synthesised from organic or inorganic sources using a range of chemical reactions including addition, oxidation and esterification ACSPH075 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - A ray model of light may be used to describe reflection, refraction and image formation from lenses and mirrors ACSPH077 Year 11 Linear Motion and Waves
Waves - The speed of light is finite and many orders of magnitude greater than the speed of mechanical waves (for example, sound and water waves); its intensity decreases in an inverse square relationship with distance from a point source ACSPH098 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Gravity and motion - The vector nature of the gravitational force can be used to analyse motion on inclined planes by considering the components of the gravitational force (that is, weight) parallel and perpendicular to the plane ACSPH103 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - A positively charged body placed in an electric field will experience a force in the direction of the field; the strength of the electric field is defined as the force per unit charge ACSPH104 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Point charges and charged objects produce an electric field in the space that surrounds them; field theory attributes the electrostatic force on a point charge or charged body to the presence of an electric field ACSPH105 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - When a charged body moves or is moved from one point to another in an electric field and its potential energy changes, work is done on or by the field
Products related to 'for'

IEC Power Supply Variable High Volt 0-300V DC
IEC 300V DC HIGH VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY
This is a special purpose compact power supply used for electrical experiments requiring smoothed, high voltage DC. The output voltage may be smoothly adjusted from zero to 300V DC or zero to 200V AC at 50mA max total load.
This ...
Order code: LB2611-001

IEC Power Supply 2 to 12V AC/DC 10A
IEC POWER SUPPLY 2-12V AC/DC 10A
This general purpose mains powered power supply is a must when a higher current output up to 10 amps AC or 8 amps DC required. Other similar power supplies like the LB2634-001, LB2633-001, LB2629-001 and LB2629C are rated up to 5 amps.
...
Order code: LB2631-001

IEC Hot Plate Thermostat PTFE Top 240V AC
IEC HOT PLATE THERMOSTAT CONTROL PTFE PLATE 240V AC
A general purpose 240V AC 600W laboratory hot plate with a 200x180mm high temperature alloy PTFE (Teflon) coated top plate for even plate temperature.
The 'Thermostat' temperature control provides continuous adjustmen...
Order code: CH1923-001

IEC Power Supply 2 to 12V AC/DC 15 Amp
IEC POWER SUPPLY 2-12V AC/DC 15A
This general purpose mains powered power supply is a robust unit designed for general laboratory use. It is suitable for most laboratory experiments where close voltage regulation and DC ripple are not important. Output is up to 12V AC or ...
Order code: LB2632-001

IEC Magnetic Stirrer Hot Plate Simmerstat Plain Top
IEC MAGNETIC STIRRER AND SIMMERSTAT HOT PLATE WITH PLAIN TOP
This unit combines the features of IEC's CH2080-001 Magnetic Stirrer and CH1920-001 'Simmerstat' Hot Plate with high temperature plain alloy top plate for even plate temperature. Heating and stirring operate tog...
Order code: CH2090-001

IEC Power Supply 100/200V DC 6.3V AC
IEC POWER SUPPLY
This low cost simple power supply is designed specifically for the Mass of an Electron experiment and is also a useful general purpose power supply where preset voltages are required. Using 12V AC input (not mains voltage), it provides multiple outputs fo...
Order code: LB2621-001

IEC Magnetic Stirrer Hot Plate Simmerstat PTFE Top
IEC MAGNETIC STIRRER AND SIMMERSTAT HOT PLATE WITH PTFE TOP
This unit combines the features of IEC's CH2081-001 Magnetic Stirrer and CH1921-001 'Simmerstat' Hot Plate with PTFE (Teflon) coated top plate to resist corrosion and for easy cleaning. Heating and stirring opera...
Order code: CH2091-001

IEC Magnetic Stirrer Hot Plate Thermostat Plain Top
IEC MAGNETIC STIRRER AND THERMOSTAT HOT PLATE WITH PLAIN TOP
This unit combines the features of IEC's CH2080-001 Magnetic Stirrer and CH1922-001 'Thermostat' Hot Plate with high temperature plain alloy top plate for even plate temperature. Heating and stirring operate tog...
Order code: CH2092-001

IEC Magnetic Stirrer Hot Plate Thermostat PTFE Top
IEC MAGNETIC STIRRER AND THERMOSTAT HOT PLATE WITH PTFE TOP
This unit combines the features of IEC's CH2081-001 Magnetic Stirrer and CH1923-001 'Thermostat' Hot Plate with PTFE (Teflon) coated top plate to resist corrosion and for easy cleaning. Heating and stirring opera...
Order code: CH2093-001

ProScope 50X Lens
PROSCOPE 50X LENS
Preferred by science educators and law enforcement investigators, the 50x lens is the best base lens to start with for almost any use.
Order code: BT-50

ProScope 1 to 10X Lens
PROSCOPE 1-10 ZOOM LENS
The most popular and versatile lens, the 1-10X is a variable focus lens that can be used as a web, still or video camera lens in 1X or manually adjusted to 10X for light magnification of text or cataloguing specimens. This lens includes illuminatin...
Order code: BT-10

Adam Mechanical Balance 2610g x 0.1g
ADAM MECHANICAL TRIPLE BEAM BALANCE 2610g x 0.1g
This Triple Beam Balance is a low cost mechanical balance that meets the requirements for high precision and reliable weighing in laboratories, schools and industry. These balances require external calibration and are usefu...
Order code: TBB 2610S

Adam Mechanical Balance 2610g x 0.1g Tare
MECHANICAL ADAM TRIPLE BEAM BALANCE 2610g x 0.1g with 225g TARE
This Triple Beam Balance is a low cost mechanical balance that meets the requirements for high precision and reliable weighing in laboratories, schools and industry. These balances require external calibratio...
Order code: TBB 2610T

Adam Electronic Balance 200g x 0.01g
Free protective cover included
ADAM ELECTRONIC BALANCE 200g x 0.01g
An easy to use and economically priced balance to suit laboratories. Includes ShockProtect™ to prevent damage from overloads up to 200kgs.
Educational Special prices currently include a free clear plastic protective cover ...
Order code: CQT 202
| Purchase QTY: (Each) | 1+ |
|---|---|
| Base price | $410.00 |
| Scientrific's price | $394.00 |
| Educational special | $328.00 |
| CLICK FOR QTY PRICING | |
| Prices exclude GST and freight | |

Adam Electronic Balance 2600g x 0.1g
Free protective cover included
ADAM ELECTRONIC BALANCE 2600g x 0.1g
An easy to use and economically priced balance to suit laboratories. Includes ShockProtect™ to prevent damage from overloads up to 200kgs.
Educational Special prices currently include a free clear plastic protective cover ...
Order code: CQT 2601
| Purchase QTY: (Each) | 1+ |
|---|---|
| Base price | $435.00 |
| Scientrific's price | $418.00 |
| Educational special | $348.00 |
| CLICK FOR QTY PRICING | |
| Prices exclude GST and freight | |

Adam Electronic Balance 600g x 0.01g
ADAM PORTABLE ELECTRONIC PRECISION BALANCE 600g x 0.01g
A versatile, portable, stackable balance suitable for use in laboratories or the field. The HandiCal™ internal calibration weight provides incredibly easy calibration without the need for external calibration weig...
Order code: HCB 602H
| Purchase QTY: (Each) | 1+ |
|---|---|
| Base price | $650.00 |
| Scientrific's price | $624.00 |
| Educational special | $520.00 |
| CLICK FOR QTY PRICING | |
| Prices exclude GST and freight | |

Adam Electronic Balance 1000g x 0.01g
ADAM PORTABLE ELECTRONIC PRECISION BALANCE 1000g x 0.01g
A versatile, portable, stackable balance suitable for use in laboratories or the field. The HandiCal™ internal calibration weight provides incredibly easy calibration without the need for external calibration wei...
Order code: HCB 1002
| Purchase QTY: (Each) | 1+ |
|---|---|
| Base price | $715.00 |
| Scientrific's price | $687.00 |
| Educational special | $572.00 |
| CLICK FOR QTY PRICING | |
| Prices exclude GST and freight | |

Adam Electronic Balance 3000g x 0.1g
ADAM PORTABLE ELECTRONIC PRECISION BALANCE 3000g x 0.1g
A versatile, portable, stackable balance suitable for use in laboratories or the field. The HandiCal™ internal calibration weight provides incredibly easy calibration without the need for external calibration weig...
Order code: HCB 3001
| Purchase QTY: (Each) | 1+ |
|---|---|
| Base price | $605.00 |
| Scientrific's price | $581.00 |
| Educational special | $484.00 |
| CLICK FOR QTY PRICING | |
| Prices exclude GST and freight | |

Dissecting and General Chemistry Laboratory Tray
DISSECTING AND GENERAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY TRAY.
A unique multipurpose tray for use in Biology and Chemistry which has been designed specifically for laboratory safety and good practice when performing dissections and chemistry experiments. Includes a replaceable Mat.
...
Order code: TRAY

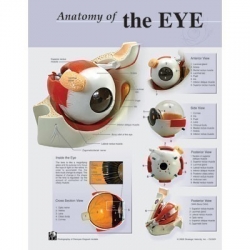
Anatomy of the Eye Poster/Chart
ANATOMY OF THE EYE POSTER/CHART
A full colour poster/chart that illustrates the anatomy of the eye in detail. Comes with metal grommets for hanging. Flexible lamination lets you write-on, wipe-off using dry erasable markers (markers not included).
Size: Approximat...
Order code: 7102-08

Biology Posters/Charts Series Set 35
COMPLETE BIOLOGY SERIES35 multi-coloured Biology Posters/Charts on a chart-head with Tripod Stand.These posters:* Are printed on tear-proof, non-yellowing stock* Highlight the Diversity of Life* Stress the complementarity of form
Order code: 1990-41

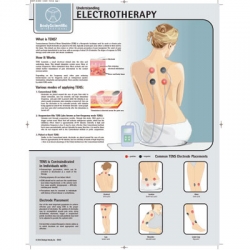
Electrotherapy Poster/Chart
ELECTROTHERAPY POSTER/CHART
This is one of the latest laminated posters available for rehabilitation and fitness. Fitness Posters have been designed to show you the main areas of anatomy and which exercises work best to help strengthen that area of the body. These posters...
Order code: 7802-08

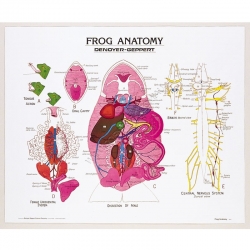
Frog Anatomy Poster/Chart
FROG ANATOMY POSTER/CHART
Three principal views detail a complete ventral dissection of a male frog, the female urogenital system and the central nervous system from the dorsal aspect. Supplementary figures show the ventral aspect of the brain and cranial nerves, oral cav...
Order code: 1891-10

Hot and Cold Therapy Poster/Chart
HOT AND COLD THERAPY POSTER/CHART
This is one of the latest laminated posters available for rehabilitation and fitness. Fitness Posters have been designed to show you the main areas of anatomy and which exercises work best to help strengthen that area of the body. These p...
Order code: 7801-08

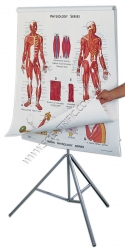
Human Physiology Posters/Charts Set of 10
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY POSTERS/CHARTS ON CHART-HEAD
A best selling series, each poster/chart features one or more principal portraits augmented by up to a dozen supplementary figures emphasising function, histological detail and perspective from a variety of aspects and magnifi...
Order code: 1400-41
424 low relevance results shown for 'for'. Prev |1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9|10|11|12|13|14|15|16|17 | Next | View 100 per page



 ,
,