347 results found for 'Electric'. |1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9|10|11|12|13|14 | Next | View 100 per page
Low relevance matches: 114 other results may be of interest to you. Show low relevance matches
Electrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU219 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Alternative Energies - Energy from a variety of sources can be used to generate electricity ACSCH030 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - Ions are atoms or groups of atoms that are electrically charged due to an imbalance in the number of electrons and protons; ions are represented by formulae which include the number of constituent atoms and the charge of the ion (for example, O2–, SO42–) ACSCH032 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The characteristic properties of metals (for example, malleability, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity) are explained by modelling metallic bonding as a regular arrangement of positive ions (cations) made stable by electrostatic forces of attra ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSPH016 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Heat transfer occurs between and within systems by conduction, convection and/or radiation ACSPH020 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Provided a substance does not change state, its temperature change is proportional to the amount of energy added to or removed from the substance; the constant of proportionality describes the heat capacity of the substance ACSPH022 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Two systems in contact transfer energy between particles so that eventually the systems reach the same temperature; that is, they are in thermal equilibrium ACSPH028 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Some nuclides are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting alpha, beta and/or gamma radiation over time until they become stable nuclides ACSPH029 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Each species of radionuclide has a specific halflife ACSPH030 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Alpha, beta and gamma radiation have sufficient energy to ionise atoms ACSPH039 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is conserved in the energy transfers and transformations that occur in an electrical circuit ACSPH040 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - The energy available to charges moving in an electrical circuit is measured using electric potential difference, which is defined as the change in potential energy per unit charge between two defined points in the circuit ACSPH041 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is required to separate positive and negative charge carriers; charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that can be used to drive current in circuits ACSPH042 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Power is the rate at which energy is transformed by a circuit component; power enables quantitative analysis of energy transformations in the circuit ACSPH043 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Resistance for ohmic and nonohmic components is defined as the ratio of potential difference across the component to the current in the component ACSPH044 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Circuit analysis and design involve calculation of the potential difference across, the current in, and the power supplied to, components in series, parallel and series/parallel circuits ACSPH137 Year 12 Revolutions in modern physics
Quantum theory - A wide range of phenomena, including black body radiation and the photoelectric effect, are explained using the concept of light quanta ACSPH108 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Magnets, magnetic materials, moving charges and currentcarrying wires experience a force in a magnetic field; this force is utilised in DC electric motors ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system ACSCH031 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The properties of ionic compounds (for example, high melting point, brittleness, ability to conduct electricity when liquid or in solution) are explained by modelling ionic bonding as ions arranged in a crystalline lattice structure with forces of attract ACSCH027 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of atoms - The type of bonding within substances explains their physical properties, including melting and boiling point, conductivity of both electricity and heat, strength and hardness ACSPH103 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - A positively charged body placed in an electric field will experience a force in the direction of the field; the strength of the electric field is defined as the force per unit charge ACSPH104 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Point charges and charged objects produce an electric field in the space that surrounds them; field theory attributes the electrostatic force on a point charge or charged body to the presence of an electric field ACSPH105 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - When a charged body moves or is moved from one point to another in an electric field and its potential energy changes, work is done on or by the field



















347 results found for 'Electric'. |1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9|10|11|12|13|14 | Next | View 100 per page
Low relevance matches: 114 other results may be of interest to you. Show low relevance matches
Curriculum resources related to 'Electric'
ACSSU097 Year 6 Physical SciencesElectrical Circuits - Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources ACSSU219 Year 6 Physical Sciences
Alternative Energies - Energy from a variety of sources can be used to generate electricity ACSCH030 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - Ions are atoms or groups of atoms that are electrically charged due to an imbalance in the number of electrons and protons; ions are represented by formulae which include the number of constituent atoms and the charge of the ion (for example, O2–, SO42–) ACSCH032 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The characteristic properties of metals (for example, malleability, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity) are explained by modelling metallic bonding as a regular arrangement of positive ions (cations) made stable by electrostatic forces of attra ACSCH108 Year 12 Equilibrium acids and redox reactions
Oxidation and reduction - Galvanic cells, including fuel cells, generate an electrical potential difference from a spontaneous redox reaction; they can be represented as cell diagrams including anode and cathode halfequations ACSPH016 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Heat transfer occurs between and within systems by conduction, convection and/or radiation ACSPH020 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Provided a substance does not change state, its temperature change is proportional to the amount of energy added to or removed from the substance; the constant of proportionality describes the heat capacity of the substance ACSPH022 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Two systems in contact transfer energy between particles so that eventually the systems reach the same temperature; that is, they are in thermal equilibrium ACSPH028 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Some nuclides are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting alpha, beta and/or gamma radiation over time until they become stable nuclides ACSPH029 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Each species of radionuclide has a specific halflife ACSPH030 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Ionising radiation and nuclear reactions - Alpha, beta and gamma radiation have sufficient energy to ionise atoms ACSPH039 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is conserved in the energy transfers and transformations that occur in an electrical circuit ACSPH040 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - The energy available to charges moving in an electrical circuit is measured using electric potential difference, which is defined as the change in potential energy per unit charge between two defined points in the circuit ACSPH041 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Energy is required to separate positive and negative charge carriers; charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that can be used to drive current in circuits ACSPH042 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Power is the rate at which energy is transformed by a circuit component; power enables quantitative analysis of energy transformations in the circuit ACSPH043 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Resistance for ohmic and nonohmic components is defined as the ratio of potential difference across the component to the current in the component ACSPH044 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Electrical circuits - Circuit analysis and design involve calculation of the potential difference across, the current in, and the power supplied to, components in series, parallel and series/parallel circuits ACSPH137 Year 12 Revolutions in modern physics
Quantum theory - A wide range of phenomena, including black body radiation and the photoelectric effect, are explained using the concept of light quanta ACSPH108 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Magnets, magnetic materials, moving charges and currentcarrying wires experience a force in a magnetic field; this force is utilised in DC electric motors ACSPH021 Year 11 Thermal nuclear and electrical physics
Heating processes - Change of state involves internal energy changes to form or break bonds between atoms or molecules; latent heat is the energy required to be added to or removed from a system to change the state of the system ACSCH031 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of materials - The properties of ionic compounds (for example, high melting point, brittleness, ability to conduct electricity when liquid or in solution) are explained by modelling ionic bonding as ions arranged in a crystalline lattice structure with forces of attract ACSCH027 Year 11 Chemical fundamentals
Properties and structure of atoms - The type of bonding within substances explains their physical properties, including melting and boiling point, conductivity of both electricity and heat, strength and hardness ACSPH103 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - A positively charged body placed in an electric field will experience a force in the direction of the field; the strength of the electric field is defined as the force per unit charge ACSPH104 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - Point charges and charged objects produce an electric field in the space that surrounds them; field theory attributes the electrostatic force on a point charge or charged body to the presence of an electric field ACSPH105 Year 12 Gravity and electromagnetism
Electromagnetism - When a charged body moves or is moved from one point to another in an electric field and its potential energy changes, work is done on or by the field
Products related to 'Electric'

IEC Electric Motor Kit Hodson Self Build
IEC HODSON MOTOR KITS
The quality Australian designed and manufactured IEC Hodson Motor Kit includes 2 motors individually packed in sturdy plastic storage jars. Designed to teach electromagnetism and how electric motors work, the kits are simple to assemble with b...
Order code: EM2193-201


| Purchase QTY: (Set of 2) | 1+ |
|---|---|
| Scientrific's price | $55.00 |
| Educational special | $50.00 |
| CLICK FOR QTY PRICING | |
| Prices exclude GST and freight | |

Electric Motor and Gearbox Kit
This gearbox kit (shown assembled) is capable of reducing the supplied 3V motor's speed from 1200 to 3 rpm in six steps, of course other output speeds can be selected. Supplied with a gearing sheet and rubber grommets to retain gears. A practical way to learn about gearboxes.
Order code: SC5755



Electric Motor 13000 rpm 600mA
Larger heavy duty, medium speed, very high torque motor, hardened steel shaft, sintered bearings, quality brushes.
12V, 13,000 rpm at 655mA no load
At maximum efficiency:
Max. torque 267g-cm at 11193 rpm, 3.91 amps
Output 30.69 watts
Body 35.8mm dia. x 71mm, shaft 3.175 ...
Order code: SC5750



Vacuum Pump Electric 35 litres/minute
ELECTRIC VACMASTER VACUUM PUMP
This two stage pump is capable of making room temperature water boil under vacuum.
It is quiet in operation and pulls an impressive 50 micron vacuum at a fast rate of 35 litres per minute.
Portable and weighs 9kg which allows one hand...
Order code: SC8012



Hydro Electric Power Lab Dynamo
HYDRO ELECTRIC DYNAMO
A water powered dymano supplied with hoses. One side connects to the water supply, the other needs to drain into a sink pr similar. The output voltage can be switched to drive either a small motor with an attatched colour disc or a torchbulb. Voltag...
Order code: HEPL001



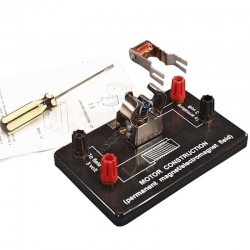
Electric Motor Construction Kit Simple
ELECTRIC MOTOR CONSTRUCTION KIT - SIMPLE.
Investigate motors with this easy to assemble hands on kit.
Made from high quality materials and designed to withstand the constant process of dismantling and assembling.
Supplied with an interchangeable field coil and field...
Order code: EM1413-01



IEC Electric Motor Generator
IEC ELECTRIC MOTOR GENERATOR 12V DC
Great for experiments in energy conversion, the IEC Electric Motor Generator Set consists of two medium sized DC electric motors securely mounted on a small base. The motors are coupled together by pulleys and a small rubber belt. The p...
Order code: EM1759-001



IEC Electric Motor and Generator Kit
IEC SMALL MOTOR/GENERATOR KIT WITH PULLEY
The IEC small electric motor/generator is a robust 3V DC motor mounted on a compact plastic base with 4mm socket head connection terminals. The motor is fitted with a small metal two step pulley with large width grooves.
Clampe...
Order code: EM1760-001



IEC Clinostat Electric on Stand
IEC ELECTRIC CLINOSTAT ON STAND
The IEC Clinostat is an instrument for the close study of small plants growing from seeds and shoots. It consists of a rugged motor rotating at 4 turns/hour that turns a sponge platform with a transparent cover. Various plants and shoots ca...
Order code: LB0870-001

IEC Kinetic Theory Model Electric
IEC KINETIC THEORY MODEL ELECTRIC 12V DC
The IEC Kinetic Theory apparatus simulates the behaviour of a gas. A strong DC motor is connected to a vibrating rubber faced platform inside an acrylic tube with a scale. A quantity of small stainless steel balls loaded into the t...
Order code: MF1990-001



IEC Electric Motor Generator Kit Spare Pulley
IEC MOTOR/GENERATOR SPARE DOUBLE PULLEY
A replacement spare double aluminium pulley with lock screw for the EM1760-001 IEC Electric Motor/Generator Kit.
Order code: PA1760-003



IEC Electric Motor Kit Hodson Magnet Only
IEC HODSON MOTOR KIT MAGNET
A replacement 50x22x6mm ceramic magnet for the EM2193-201 IEC Hodson Motor Kit.
Each motor kit is supplied with 2 of these magnets to create the field for the motor to run.
Order code: PA2193-210



IEC Electric Motor Kit Hodson Roll of Wire Black
IEC HODSON MOTOR KIT ROLL OF BLACK WIRE
A replacement small reel of 0.5mmD black bell wire for winding rotor coils with the EM2193-201 IEC Hodson Motor Kit.
Order code: PA2193-211



IEC Electric Motor Kit Hodson Roll of Wire Red
IEC HODSON MOTOR KIT ROLL OF RED WIRE
A replacement small reel of 0.5mmD red bell wire for winding rotor coils with the EM2193-201 IEC Hodson Motor Kit.
Order code: PA2193-212



IEC Electric Motor Kit Hodson Rotor Shaft
IEC HODSON MOTOR KIT ROTOR SHAFT
A replacement rotor shaft for the EM2193-201 IEC Hodson Motor Kit.
The rotor shaft fits the rotor into the two end plates.
Order code: PA2193-220



IEC Electric Motor Kit Hodson Rubber Ring
IEC HODSON MOTOR KIT RUBBER RING
A replacement rubber ring for forming the commutator for the EM2193-201 IEC Hodson Motor Kit.
The rings hold the bare ends of the rotor winding tightly to the central boss to form the commutator.
Order code: PA2193-230


IEC Photo Electric Effect Light Scope 12V Old
PHOTO-ELECTRIC EFFECT OLD MODEL 12V LIGHT SOURCE
A replacement 12V light source for the OLD MODEL IEC Photoelectric Effect and Planck's Constant. The light source has a foot, cable with 2 x banana plugs and rests on table behind the instrument.
NOTE: The later...
Order code: PA2340-003
IEC Photo Electric Effect Light Source 12V Slide-in
IEC PHOTO-ELECTRIC EFFECT LIGHT SOURCE 12V SLIDE-IN
A replacement 12V light source for the AP2341-002 IEC Photoelectric Effect and Planck's Constant.
With a 'QI' lamp and cable with 2 x banana plugs, the light source is designed to lock to the rear face of the instrument...
Order code: PA2341-004
IEC Photo Electric Effect Standard Grad Filters
Discontinued - only 3 sets in stock
IEC PHOTO-ELECTRIC EFFECT STANDARD GRADUATED FILTERS
A set of 5 standard graduated filters (red, orange, yellow, green, blue) that slide into the retainer at the rear of the IEC Photoelectric Effect and Planck's Constant instrument to perform the required experiments. Eac...
Order code: PA2341-010
IEC Photo Electric Effect Tube Only Spare
IEC PHOTO-ELECTRIC EFFECT TUBE ONLY
A replacement tube only with special characteristics to suit the wavelengths being studied by the IEC Photoelectric Effect and Planck's Constant apparatus.
Order code: PA2341-020

Electric Motor 3600rpm 25mA Solar Pack of 10
Last pack
This small electric motor is specially made to be run from solar cells. Use for solar cell experiments or as a replacement motor in solar model kits. 1.5 - 3V DC, 3,600 rpm at 25mA no load, body 23 dia. x 27mm, shaft 2 x 6.5mm, max. torque 1.8g-cm.
Order code: SC4422



Educational Solar Energy Kit
Educational Solar Energy Kit.
The best educational and most economical solar energy kit that we've ever stocked.
Eight separate solar cells are mounted in a sturdy plastic frame, each cell can be connected to adjoining cells using sturdy metal links to increase either ...
Order code: SC52400


| Purchase QTY: (Each) | 1+ |
|---|---|
| Base price | $22.00 |
| Scientrific's price | $20.00 |
| Educational special | $15.50 |
| CLICK FOR QTY PRICING | |
| Prices exclude GST and freight | |

Reverse Osmosis Deioniser System
A deioniser is a great replacement for a traditional, energy wasting electric still as deionisers use no electricity or cooling water.
Our Reverse Osmosis Deioniser has been specially built for us and has a 3 step deionisation process that uses a carbon filter, a reverse osmos...
Order code: SC93010

IEC Motor Generator Hand Cranked AC/DC
IEC HAND DRIVEN MOTOR/GENERATOR
A compact and strongly built DC electric Motor/Generator that can be hand wound by wheel and belt. The belt is easily removed when running as a DC Motor. Can run using a permanent 'U' shaped magnet or by fitting into the U core as part of ...
Order code: EM1758-001


347 results found for 'Electric'. |1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9|10|11|12|13|14 | Next | View 100 per page


